Play-based learning is a core principle of the EYLF, emphasizing that children learn best through exploration, curiosity, and meaningful interactions. It allows children to develop problem-solving skills, creativity, and social-emotional intelligence in a natural and engaging way. The following article provides information on Key Aspects of Play-Based Learning in EYLF, How EYLF Links to Play-Based Learning, What Are Some Effective Strategies For Play-Based Learning and more.
Key Aspects of Play-Based Learning in EYLF
- Child-Led Exploration: Children take the lead in their learning, following their interests and ideas.
- Intentional Teaching: Educators thoughtfully guide and extend children's learning through play.
- Holistic Development: Play supports cognitive, social, emotional, and physical growth.
- Active Engagement: Children construct their own understanding by interacting with their environment.
How EYLF Links to Play-Based Learning
-
Learning Outcomes Alignment
- Play-based experiences help children develop a strong sense of identity (Outcome 1).
- Through play, children connect with and contribute to their world (Outcome 2).
- Play supports well-being by encouraging movement, self-expression, and emotional regulation (Outcome 3).
- It fosters confidence and involvement in learning (Outcome 4).
- Play enhances communication skills through storytelling, role-playing, and interaction (Outcome 5).
-
Intentional Teaching in Play
- Educators can observe, guide, and extend children's learning through play.
- Providing open-ended materials encourages creativity and problem-solving.
- Recognizing children's unique interests helps tailor play experiences to their developmental needs.
-
Creating a Play-Based Environment
- Thoughtful planning ensures play spaces are engaging and meaningful.
- Encouraging collaborative play builds social skills and emotional intelligence.
- Sensory-rich experiences enhance learning and brain development.
What Are Some Effective Strategies For Play-Based Learning
Play-based learning thrives when children are engaged, curious, and encouraged to explore. Here are some effective strategies to implement it successfully:
1. Child-Led Play
-
Allow children to take the lead in their learning experiences.
-
Observe their interests and build activities around them.
2. Open-Ended Materials
-
Provide loose parts like blocks, fabric, and natural materials.
-
Encourage creativity and problem-solving.
3. Intentional Teaching Moments
-
Guide learning through thoughtful questioning and prompts.
-
Extend play by introducing new concepts naturally.
4. Social Play & Collaboration
-
Foster teamwork through group activities and role-playing.
-
Encourage communication and emotional intelligence.
5. Sensory Play
-
Use textures, sounds, and movement to enhance engagement.
-
Activities like water play, sand exploration, and messy play build cognitive skills.
6. Storytelling & Dramatic Play
-
Encourage children to act out stories or create their own narratives.
-
Helps with language development and imagination.
7. STEAM-Based Play
-
Integrate science, technology, engineering, arts, and math into play.
-
Simple experiments, building challenges, and creative projects make learning fun.
Further Reading
The Value of Play Based Learning
Spontaneous Play In Early Childhood
How Play Based Learning Supports School Readiness
The Value Of Play
Play Principles







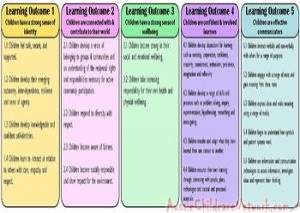 Here is the list of the EYLF Learning Outcomes that you can use as a guide or reference for your documentation and planning. The EYLF
Here is the list of the EYLF Learning Outcomes that you can use as a guide or reference for your documentation and planning. The EYLF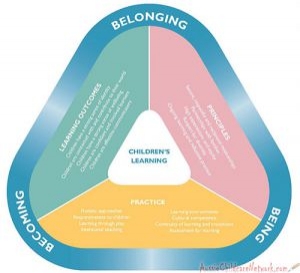 The EYLF is a guide which consists of Principles, Practices and 5 main Learning Outcomes along with each of their sub outcomes, based on identity,
The EYLF is a guide which consists of Principles, Practices and 5 main Learning Outcomes along with each of their sub outcomes, based on identity, This is a guide on How to Write a Learning Story. It provides information on What Is A Learning Story, Writing A Learning Story, Sample
This is a guide on How to Write a Learning Story. It provides information on What Is A Learning Story, Writing A Learning Story, Sample One of the most important types of documentation methods that educators needs to be familiar with are “observations”. Observations are crucial for all early childhood
One of the most important types of documentation methods that educators needs to be familiar with are “observations”. Observations are crucial for all early childhood To support children achieve learning outcomes from the EYLF Framework, the following list gives educators examples of how to promote children's learning in each individual
To support children achieve learning outcomes from the EYLF Framework, the following list gives educators examples of how to promote children's learning in each individual Reflective practice is learning from everyday situations and issues and concerns that arise which form part of our daily routine while working in an early
Reflective practice is learning from everyday situations and issues and concerns that arise which form part of our daily routine while working in an early Within Australia, Programming and Planning is reflected and supported by the Early Years Learning Framework. Educators within early childhood settings, use the EYLF to guide
Within Australia, Programming and Planning is reflected and supported by the Early Years Learning Framework. Educators within early childhood settings, use the EYLF to guide When observing children, it's important that we use a range of different observation methods from running records, learning stories to photographs and work samples. Using
When observing children, it's important that we use a range of different observation methods from running records, learning stories to photographs and work samples. Using This is a guide for educators on what to observe under each sub learning outcome from the EYLF Framework, when a child is engaged in
This is a guide for educators on what to observe under each sub learning outcome from the EYLF Framework, when a child is engaged in The Early Years Learning Framework describes the curriculum as “all the interactions, experiences, activities, routines and events, planned and unplanned, that occur in an environment
The Early Years Learning Framework describes the curriculum as “all the interactions, experiences, activities, routines and events, planned and unplanned, that occur in an environment


