Here's a comprehensive breakdown of Exceeding Theme 2:Practice is Informed by Critical Reflection across all quality areas 1 to 7 of the National Quality Standard (NQS). This theme emphasizes how services use deep, ongoing reflection to inform and improve their practices—not just occasionally, but as a core part of their culture.
Quality Area 1: Educational Program and Practice
Overview
Critical reflection drives curriculum decisions, ensuring learning is responsive, inclusive, and grounded in theory and evidence.
-
Example 1: Educators reflect on how daily routines impact children’s learning outcomes.
Implementation: Weekly team meetings include discussions on how transitions and routines can better support learning and agency. -
Example 2: The team revisits curriculum decisions in light of children’s evolving interests.
Implementation: Educators use reflective journals and planning cycles to adapt programs based on observations and feedback.
Quality Area 2: Children’s Health and Safety
Overview
Health and safety practices are refined through regular analysis of incidents, feedback, and current guidance.
-
Example 1: Educators reflect on sleep and rest routines to ensure cultural sensitivity and individual comfort.
Implementation: Feedback from families and staff informs adjustments to sleep environments and schedules. -
Example 2: Risk assessments are reviewed after every incident or drill.
Implementation: Monthly safety audits include reflective discussions on what worked and what could be improved.
Quality Area 3: Physical Environment
Overview
The design and use of spaces evolve through reflection on children’s engagement, accessibility, and safety.
-
Example 1: Educators reflect on how indoor/outdoor spaces support different learning styles.
Implementation: Observations and child feedback guide changes to layout and materials. -
Example 2: Sustainability practices are reviewed for effectiveness and child involvement.
Implementation: Staff reflect on how children engage with recycling and gardening and adjust strategies accordingly.
Quality Area 4: Staffing Arrangements
Overview
Staffing decisions are informed by reflective practice to ensure continuity, collaboration, and professional growth.
-
Example 1: Educators reflect on team dynamics and communication.
Implementation: Regular peer feedback sessions help identify strengths and areas for improvement. -
Example 2: Induction processes are reviewed to better support new staff.
Implementation: New educators participate in reflective check-ins to share their onboarding experience and suggest improvements.
Quality Area 5: Relationships with Children
Overview
Interactions with children are shaped by reflection on emotional needs, communication styles, and developmental stages.
-
Example 1: Educators reflect on how their responses support children’s emotional regulation.
Implementation: Staff use case studies and role-play to explore alternative strategies for co-regulation. -
Example 2: Reflection on children’s voices in decision-making.
Implementation: Educators analyze how children’s input is used in planning and adjust practices to enhance agency.
Quality Area 6: Collaborative Partnerships with Families and Communities
Overview
Family and community engagement is strengthened through reflection on communication, inclusion, and shared decision-making.
-
Example 1: Educators reflect on how well family feedback is incorporated into the curriculum.
Implementation: Planning documents are reviewed to ensure visible links to family input. -
Example 2: Community partnerships are evaluated for relevance and impact.
Implementation: Staff reflect on the outcomes of community visits and adjust future collaborations accordingly.
Quality Area 7: Governance and Leadership
Overview
Leadership practices and governance structures evolve through reflective analysis of service performance and team input.
-
Example 1: Leaders reflect on how policies support educator well-being and quality practice.
Implementation: Staff surveys and reflective forums inform updates to HR and operational policies. -
Example 2: The Quality Improvement Plan (QIP) is reviewed collaboratively.
Implementation: Reflection sessions are built into staff meetings to ensure the QIP is a living document, not a static report.
Further Reading
Exceeding Theme 1 Across Quality Areas 1 to 7
Exceeding Guidance For Quality Area 1
Exceeding Guidance For Quality Area 2
Exceeding Guidance For Quality Area 3
Exceeding Guidance For Quality Area 4
Exceeding Guidance For Quality Area 5
Exceeding Guidance For Quality Area 6
Exceeding Guidance For Quality Area 7







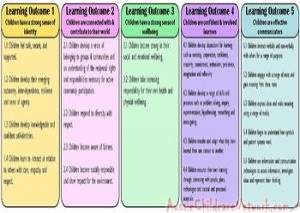 Here is the list of the EYLF Learning Outcomes that you can use as a guide or reference for your documentation and planning. The EYLF
Here is the list of the EYLF Learning Outcomes that you can use as a guide or reference for your documentation and planning. The EYLF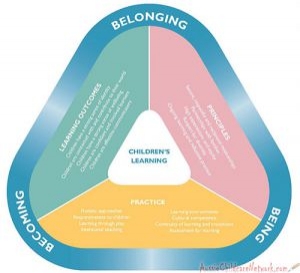 The EYLF is a guide which consists of Principles, Practices and 5 main Learning Outcomes along with each of their sub outcomes, based on identity,
The EYLF is a guide which consists of Principles, Practices and 5 main Learning Outcomes along with each of their sub outcomes, based on identity, This is a guide on How to Write a Learning Story. It provides information on What Is A Learning Story, Writing A Learning Story, Sample
This is a guide on How to Write a Learning Story. It provides information on What Is A Learning Story, Writing A Learning Story, Sample One of the most important types of documentation methods that educators needs to be familiar with are “observations”. Observations are crucial for all early childhood
One of the most important types of documentation methods that educators needs to be familiar with are “observations”. Observations are crucial for all early childhood To support children achieve learning outcomes from the EYLF Framework, the following list gives educators examples of how to promote children's learning in each individual
To support children achieve learning outcomes from the EYLF Framework, the following list gives educators examples of how to promote children's learning in each individual Reflective practice is learning from everyday situations and issues and concerns that arise which form part of our daily routine while working in an early
Reflective practice is learning from everyday situations and issues and concerns that arise which form part of our daily routine while working in an early Within Australia, Programming and Planning is reflected and supported by the Early Years Learning Framework. Educators within early childhood settings, use the EYLF to guide
Within Australia, Programming and Planning is reflected and supported by the Early Years Learning Framework. Educators within early childhood settings, use the EYLF to guide When observing children, it's important that we use a range of different observation methods from running records, learning stories to photographs and work samples. Using
When observing children, it's important that we use a range of different observation methods from running records, learning stories to photographs and work samples. Using This is a guide for educators on what to observe under each sub learning outcome from the EYLF Framework, when a child is engaged in
This is a guide for educators on what to observe under each sub learning outcome from the EYLF Framework, when a child is engaged in The Early Years Learning Framework describes the curriculum as “all the interactions, experiences, activities, routines and events, planned and unplanned, that occur in an environment
The Early Years Learning Framework describes the curriculum as “all the interactions, experiences, activities, routines and events, planned and unplanned, that occur in an environment


