

Early childhood education is facing a crisis that cannot be solved with more training modules or compliance checklists. Educators are not leaving because they lack skills or passion. They are leaving because they are being treated as expendable, micromanaged to exhaustion, and denied the respect they deserve as professionals and as people.
The recent announcement by Minister for Education Jason Clare that childcare centres will receive funding to close early for mandatory child safety training. But let’s be clear—child protection training is not new. Educators already undertake annual courses and ongoing professional development throughout the year. You cannot work in this industry without it. Training is essential, but it is not where the real problems begin.
Child protection courses are already mandatory. The real crisis?
Too many children per educator
Understaffed centres
Lack of inclusion support for children with disabilities
Until ratios drop and staffing rises, training alone won’t fix child safety.
Australia’s Early Childhood Education and Care (ECEC) sector is facing a crisis that numbers alone cannot explain. On paper, more than 70,000 students are enrolled in early childhood qualifications across the country. Yet services report a shortfall of 21,000 qualified educators. Families are stuck on waitlists, centres are forced to reduce hours, and educators already in the field are stretched to breaking point.
This paradox—so many in training, yet so few in classrooms—reveals a deeper structural failure.
At first glance, the idea of asking a baby for consent before a nappy change might sound absurd. After all, babies can’t speak, reason, or give informed permission. But beneath the surface, this question invites us to reflect on something deeper: How do we model respect, autonomy, and emotional safety from the very beginning of life?
In early childhood education, qualifications are often seen as the benchmark of quality. Diplomas, degrees, and certificates line the walls of centres, signaling compliance and professional achievement. Yet research consistently shows that what truly shapes a child’s well-being and learning is not the paper on the wall, but the warmth, trust, and attunement in the relationships they experience every day.
In early childhood settings, every child deserves to be seen, heard, and held in emotionally safe environments. But when group sizes swell beyond developmental best practice, connection suffers, and so does care.
Large groups can dilute relationships, overwhelm educators, and compromise inclusion. Babies need calm, responsive spaces. Toddlers thrive in predictable, nurturing environments. Preschoolers flourish when their voices are heard—not lost in the crowd.
Across the globe, countries like New Zealand and Denmark cap group sizes to protect developmental well-being. In Australia, while ratios are regulated, group sizes often exceed what’s optimal, especially for infants and children with additional needs.
It’s time to ask: How many is too many?
And more importantly: What does quality care truly require?
Under ACECQA’s National Quality Framework, educators are deemed “qualified” if they hold a Certificate III, Diploma, or approved university degree. But qualification does not equal competence. The current system allows individuals with unrelated undergraduate degrees to complete a one-year postgraduate course and enter classrooms, often with minimal practical experience or emotional readiness. The result? A workforce flooded with technically qualified but emotionally disconnected practitioners some of whom openly admit they “don’t like kids” and entered the profession for visa access or job security.
In our push to capture every moment under the EYLF, many educators find themselves swamped by paperwork rather than immersed in play. Observation records, plans, reflections, assessments—they grow faster than we can connect with each child. When every anecdote demands multiple frameworks and sign-offs, learning narratives can lose their heart. In today’s landscape, dominated by the Early Years Learning Framework (EYLF), that balance has unraveled. The EYLF was meant to unify and elevate practice. Instead, we’ve watched it morph into an overwhelming checklist culture—where paperwork eclipses presence, and compliance overshadows connection. Somewhere along the way, a valuable framework was repurposed into a bureaucratic beast. So, educators, are we documenting learning or drowning in it?
Across Australia, regulated staffing ratios aim to safeguard children in early learning settings. However, a growing number of incidents reveal that meeting these minimum requirements on paper doesn’t always translate into active, vigilant supervision. Below are several case studies that illustrate how gaps can emerge—even when legal ratios are nominally met.
The “under the roof” rule allows childcare centres to meet staffing ratios by counting all educators on-site, regardless of whether they are physically present in rooms with children. This means a centre may appear compliant on paper, even if individual rooms are understaffed.While originally intended to offer flexibility, educators say it’s now being used to cut corners—leaving children without adequate supervision and educators stretched beyond capacity.
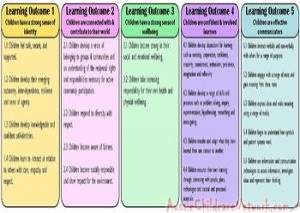 Here is the list of the EYLF Learning Outcomes that you can use as a guide or reference for your documentation and planning. The EYLF… Read More
Here is the list of the EYLF Learning Outcomes that you can use as a guide or reference for your documentation and planning. The EYLF… Read More
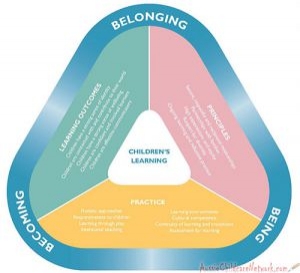 The EYLF is a guide which consists of Principles, Practices and 5 main Learning Outcomes along with each of their sub outcomes, based on identity,… Read More
The EYLF is a guide which consists of Principles, Practices and 5 main Learning Outcomes along with each of their sub outcomes, based on identity,… Read More
 This is a guide on How to Write a Learning Story. It provides information on What Is A Learning Story, Writing A Learning Story, Sample… Read More
This is a guide on How to Write a Learning Story. It provides information on What Is A Learning Story, Writing A Learning Story, Sample… Read More
 One of the most important types of documentation methods that educators needs to be familiar with are “observations”. Observations are crucial for all early childhood… Read More
One of the most important types of documentation methods that educators needs to be familiar with are “observations”. Observations are crucial for all early childhood… Read More
 To support children achieve learning outcomes from the EYLF Framework, the following list gives educators examples of how to promote children's learning in each individual… Read More
To support children achieve learning outcomes from the EYLF Framework, the following list gives educators examples of how to promote children's learning in each individual… Read More
 Reflective practice is learning from everyday situations and issues and concerns that arise which form part of our daily routine while working in an early… Read More
Reflective practice is learning from everyday situations and issues and concerns that arise which form part of our daily routine while working in an early… Read More
 Within Australia, Programming and Planning is reflected and supported by the Early Years Learning Framework. Educators within early childhood settings, use the EYLF to guide… Read More
Within Australia, Programming and Planning is reflected and supported by the Early Years Learning Framework. Educators within early childhood settings, use the EYLF to guide… Read More
 When observing children, it's important that we use a range of different observation methods from running records, learning stories to photographs and work samples. Using… Read More
When observing children, it's important that we use a range of different observation methods from running records, learning stories to photographs and work samples. Using… Read More
 This is a guide for educators on what to observe under each sub learning outcome from the EYLF Framework, when a child is engaged in… Read More
This is a guide for educators on what to observe under each sub learning outcome from the EYLF Framework, when a child is engaged in… Read More
 The Early Years Learning Framework describes the curriculum as “all the interactions, experiences, activities, routines and events, planned and unplanned, that occur in an environment… Read More
The Early Years Learning Framework describes the curriculum as “all the interactions, experiences, activities, routines and events, planned and unplanned, that occur in an environment… Read More

World Space Week is from 4th - 10th October. To help educators join the global celebration...
See more...
The My Outdoor Classroom Nature Passport package supports educators in taking children outdoors for enriched play-based learning...
See more...
In early childhood education, documentation is often framed as evidence or proof of learning, compliance...
See more...© 2009-2025 Aussie Childcare Network Pty Ltd. All Rights Reserved.

