Writing critical reflections for the National Quality Standards (NQS) in early childhood education involves a thoughtful and systematic approach to evaluating and improving your teaching practices. The following articlr provides information on Steps to Write Critical Reflections For The NQS, Critical Reflection Examples for Quality Area 1 To Quality Area 7 and more.
Steps to Write Critical Reflections For The NQS
-
Identify the Focus: Determine the specific aspect of your practice you want to reflect on. This could be a particular event, interaction, or overall teaching strategy.
-
Gather Information: Collect relevant information about the focus area. This might include observations, children's work, feedback from colleagues, and your own experiences.
-
Analyze and Evaluate: Examine the information from multiple perspectives. Consider how your actions align with the NQS and other relevant frameworks. Ask yourself questions like:
-
What went well?
-
What didn't go well?
-
Why did it happen?
-
How did it impact children's learning and development?
-
What could be improved?
-
-
Link to Standards: Relate your reflections to the NQS and other relevant standards. Highlight how your practices support the quality areas and elements outlined in the NQS.
-
Plan for Improvement: Based on your analysis, develop an action plan to address areas for improvement. Set specific, achievable goals and outline the steps you will take to implement changes.
-
Document Your Reflections: Keep a reflective journal or use digital tools to document your reflections regularly. Record significant events, interactions, and observations, and analyze them critically.
-
Seek Feedback: Share your reflections with colleagues, supervisors, and families. Use their feedback to inform your reflections and make continuous improvements.
-
Review and Adjust: Regularly review your reflections and action plans. Monitor your progress and adjust your plans as needed to ensure continuous improvement.
Example Reflection
Focus: Reflecting on a challenging interaction with a child displaying aggressive behavior.
Information Gathered: Observation notes, feedback from colleagues, and your own feelings during the interaction.
Analysis and Evaluation:
-
What went well: I remained calm and used a calm voice to address the child.
-
What didn't go well: I struggled to find an effective strategy to de-escalate the situation quickly.
-
Why did it happen? The child was experiencing frustration due to a lack of understanding of the task.
-
How did it impact children's learning and development? The child's aggressive behavior disrupted the learning environment for others.
-
What could be improved: I could use more proactive strategies to prevent frustration and provide clearer instructions.
Plan for Improvement:
-
Attend a workshop on managing challenging behaviors.
-
Implement a visual schedule to help children understand the daily routine.
-
Use positive reinforcement to encourage appropriate behavior.
By following these steps, you can create meaningful and impactful critical reflections that contribute to the continuous improvement of your practice and the quality of education and care you provide.
Critical Reflection Example for Quality Area 1: Educational Program and Practice
Focus: Reflecting on the implementation of a child-centered activity based on children's interests and how it aligns with Quality Area 1.
Information Gathered:
-
Observation notes on children's engagement and interactions during the activity.
-
Feedback from colleagues on the planning and execution of the activity.
-
Children’s work and their verbal and non-verbal responses during the activity.
Description of the Activity: The activity was based on children's interest in nature and gardening. We set up a mini-garden project where children could plant seeds, water them, and observe the growth process. The project included hands-on activities, storytelling about plants, and art projects related to gardening.
Analysis and Evaluation:
-
What went well: The children were highly engaged and excited about the project. They demonstrated curiosity and asked many questions about the plants. The activity encouraged teamwork and collaboration as children worked together to take care of the garden.
-
What didn't go well: Some children struggled with the waiting period for the seeds to sprout, leading to moments of frustration and impatience.
-
Why did it happen: The delay in seeing immediate results may have been difficult for some children to understand. Additionally, not all children had the same level of interest in gardening.
-
How did it impact children's learning and development: The activity supported children's learning in several areas, including science (understanding plant growth), responsibility (taking care of the garden), and social skills (working together). However, the frustration experienced by some children indicated a need for more immediate, short-term activities to maintain their interest.
-
What could be improved: Incorporating additional activities that provide more immediate gratification, such as quick-growing plants or related art projects that can be completed in a shorter time frame.
Link to Standards:
-
Element 1.1.1: Approved learning framework: The activity was aligned with the Early Years Learning Framework (EYLF), supporting outcomes related to children's sense of identity and their connection with the natural world.
-
Element 1.1.2: Child-centred: The project was based on children's expressed interests in nature and gardening, making the learning experience relevant and engaging for them.
-
Element 1.1.3: Program learning opportunities: The mini-garden project provided diverse learning opportunities, including hands-on activities, storytelling, and art projects.
Plan for Improvement:
-
Immediate Steps: Introduce a variety of activities within the gardening project that offer quicker results, such as planting fast-growing herbs or creating instant art projects related to plants.
-
Long-term Goals: Incorporate more child-centered projects that cater to different interests and learning styles. Plan activities that balance long-term projects with short-term activities to keep all children engaged.
-
Professional Development: Attend workshops on integrating nature-based learning in early childhood education and collaborate with colleagues to share ideas and best practices.
Review and Adjust:
-
Regularly review children's engagement and feedback to adjust activities as needed.
-
Continue to reflect on the effectiveness of child-centered projects and seek ways to enhance their impact on children's learning and development.
By critically reflecting on this activity, I can ensure continuous improvement in providing a stimulating and engaging educational program that aligns with Quality Area 1 of the NQS.
Critical Reflection Example for Quality Area 2: Children's Health and Safety
Focus: Reflecting on the implementation of health and safety practices during outdoor playtime and how it aligns with Quality Area 2.
Information Gathered:
-
Observation notes on children's behavior and activities during outdoor playtime.
-
Feedback from colleagues on the supervision and safety measures in place.
-
Incident reports, if any, and first aid records.
-
Input from children and families regarding outdoor playtime experiences.
Description of the Activity: Outdoor playtime is scheduled for an hour each day, providing children with opportunities for physical activity, exploration, and social interaction. The play area includes a variety of equipment such as swings, slides, climbing structures, and a sandpit.
Analysis and Evaluation:
-
What went well: Children were actively engaged in physical play, demonstrating gross motor skills and social interactions. Educators effectively supervised the children, ensuring that safety rules were followed.
-
What didn't go well: A few minor incidents occurred where children tripped and fell, leading to minor injuries. Some children showed signs of overheating and dehydration during particularly warm days.
-
Why did it happen: The minor injuries were due to uneven surfaces and the high activity levels of the children. The overheating and dehydration were likely due to insufficient hydration and sun protection measures.
-
How did it impact children's learning and development: The outdoor playtime supported children's physical development and social skills. However, the minor injuries and overheating incidents indicated a need for improved safety measures to ensure children's well-being.
-
What could be improved: Regular checks and maintenance of the play area to ensure safe surfaces. Implementing better hydration and sun protection practices, such as scheduled water breaks and ensuring all children wear hats and sunscreen.
Link to Standards:
-
Element 2.1.1: Wellbeing and comfort: Ensuring that children's physical health is supported by providing safe and comfortable environments. This includes maintaining safe play areas and ensuring children are protected from the sun.
-
Element 2.1.2: Health practices and procedures: Implementing effective hygiene practices and promoting healthy lifestyles. This includes encouraging regular hydration and sun protection during outdoor play.
-
Element 2.2.1: Supervision: Supervising children at all times to ensure their safety. This involves active monitoring and intervention to prevent accidents and injuries.
Plan for Improvement:
-
Immediate Steps: Conduct a thorough inspection of the outdoor play area to identify and address any safety hazards. Schedule regular maintenance checks to ensure ongoing safety.
-
Long-term Goals: Develop and implement a comprehensive sun protection policy that includes mandatory hat-wearing, sunscreen application, and scheduled water breaks. Educate children and families on the importance of sun safety and hydration.
-
Professional Development: Attend workshops on playground safety and sun protection in early childhood settings. Collaborate with colleagues to share best practices and develop consistent safety protocols.
Review and Adjust:
-
Regularly review incident reports and feedback to identify patterns and areas for improvement.
-
Continuously reflect on the effectiveness of health and safety practices and make adjustments as needed to ensure the well-being of all children.
By critically reflecting on these health and safety practices, I can ensure continuous improvement in providing a safe and healthy environment for children, aligned with Quality Area 2 of the NQS.
Critical Reflection Example for Quality Area 3: Physical Environment
Focus: Reflecting on the setup and use of indoor and outdoor learning environments and how they align with Quality Area 3.
Information Gathered:
-
Observation notes on children's interactions with the environment and materials.
-
Feedback from colleagues and families on the layout and resources.
-
Incident reports related to environmental safety.
-
Children's feedback and preferences regarding different play areas.
Description of the Environment: The indoor learning environment includes various play stations such as a reading corner, art area, building block area, and role-play corner. The outdoor environment features a playground with climbing structures, a sandpit, a garden, and open space for physical activities.
Analysis and Evaluation:
-
What went well: Children were observed actively engaging with different play stations, showing creativity and collaboration. The outdoor environment provided opportunities for physical activity and exploration.
-
What didn't go well: Certain areas, such as the reading corner, were underutilized. There were occasional conflicts over the use of popular equipment in the playground.
-
Why did it happen: The reading corner may not have been as inviting or accessible as other play areas. Conflicts over equipment may have arisen due to a lack of sufficient resources or structured turn-taking strategies.
-
How did it impact children's learning and development: The varied play stations supported different areas of learning, such as literacy, creativity, and physical development. However, the underutilized reading corner indicated a missed opportunity for promoting early literacy skills.
-
What could be improved: Making the reading corner more inviting by adding comfortable seating, a wider selection of books, and incorporating storytelling sessions. Implementing strategies to manage conflicts over equipment, such as introducing a sign-up system or rotating play schedules.
Link to Standards:
-
Element 3.1.1: Fit for purpose: Ensuring that the design and location of the premises are appropriate for the operation of a service. This includes creating engaging and accessible indoor and outdoor spaces that meet the needs of children.
-
Element 3.2.1: Inclusive environment: Designing and arranging spaces that are welcoming and inclusive. This involves ensuring that all children can participate in activities regardless of their abilities.
-
Element 3.2.2: Resources support play-based learning: Providing resources, materials, and equipment that enable children to engage in meaningful play and exploration. This includes a variety of play stations and outdoor equipment.
Plan for Improvement:
-
Immediate Steps: Redesign the reading corner with input from children and families to make it more inviting. Introduce more comfortable seating, a broader range of books, and regular storytelling sessions.
-
Long-term Goals: Continuously assess the indoor and outdoor environments to ensure they meet the needs and interests of children. Implement strategies to manage conflicts over equipment, such as rotating play schedules or providing duplicate resources.
-
Professional Development: Attend workshops on creating engaging learning environments and inclusive practices. Collaborate with colleagues to share ideas and best practices for setting up play areas.
Review and Adjust:
-
Regularly review the utilization of different play areas and gather feedback from children, families, and colleagues.
-
Reflect on the effectiveness of changes made to the environment and make adjustments as needed to ensure it remains engaging, inclusive, and supportive of children's learning and development.
By critically reflecting on the physical environment, I can ensure continuous improvement in providing a safe, engaging, and inclusive space for children, aligned with Quality Area 3 of the NQS.
Critical Reflection Example for Quality Area 4: Staffing Arrangements
Focus: Reflecting on the effectiveness of staffing arrangements and how they contribute to the quality of education and care in alignment with Quality Area 4.
Information Gathered:
-
Observation notes on staff interactions with children and each other.
-
Feedback from staff, children, and families about the staffing arrangements.
-
Staff schedules, rosters, and any records of staff meetings or training sessions.
-
Incident reports, if any, related to staffing issues.
Description of the Current Staffing Arrangement: The center operates with a team of qualified educators, including lead teachers, assistant teachers, and support staff. Staff-to-child ratios are maintained as per regulatory requirements, and staff schedules are designed to ensure adequate supervision and support throughout the day.
Analysis and Evaluation:
-
What went well: The staff-to-child ratios were consistently maintained, ensuring that children received adequate supervision and support. Staff members worked collaboratively, sharing responsibilities and supporting each other during busy times. Regular staff meetings facilitated open communication and continuous professional development.
-
What didn't go well: There were occasional instances of staff shortages due to unexpected absences, leading to increased workload and stress for remaining staff members. In some cases, staff turnover affected continuity and consistency in care and relationships with children.
-
Why did it happen: Unexpected absences and staff turnover are common challenges in early childhood settings. The increased workload during these times may have contributed to staff stress and burnout.
-
How did it impact children's learning and development: Consistent staffing arrangements provided children with stable and supportive relationships, contributing to their sense of security and well-being. However, staff shortages and turnover occasionally disrupted routines and relationships, potentially impacting children's sense of stability.
-
What could be improved: Developing a more robust system for managing unexpected absences, such as having a pool of relief staff available. Implementing strategies to improve staff retention, such as offering professional development opportunities, recognition programs, and supportive work environments.
Link to Standards:
-
Element 4.1.1: Organisation of educators: The organisation of educators is managed to ensure effective implementation of the educational program and the safety and wellbeing of children. This involves maintaining appropriate staff-to-child ratios and ensuring qualified staff are present.
-
Element 4.2.1: Professional collaboration: Educators, co-ordinators, and staff members work collaboratively and demonstrate mutual respect and support. This includes regular team meetings, shared responsibilities, and a positive work culture.
-
Element 4.2.2: Professional standards: Professional standards guide practice, interactions, and relationships. This involves adhering to ethical guidelines, maintaining professional behavior, and engaging in continuous professional development.
Plan for Improvement:
-
Immediate Steps: Create a pool of relief staff who can be called upon during unexpected absences. Develop a clear communication plan for staff to report absences and arrange coverage promptly.
-
Long-term Goals: Implement staff retention strategies, such as offering competitive salaries, professional development opportunities, and recognition programs. Foster a supportive work environment that promotes well-being and job satisfaction.
-
Professional Development: Organize workshops on team building, stress management, and effective communication. Encourage staff to pursue further education and training to enhance their skills and career development.
Review and Adjust:
-
Regularly review staff schedules, rosters, and feedback to ensure staffing arrangements are effective and supportive.
-
Continuously reflect on the impact of staffing arrangements on children's learning and development and make adjustments as needed to ensure high-quality care.
By critically reflecting on staffing arrangements, I can ensure continuous improvement in providing a supportive and effective team environment, aligned with Quality Area 4 of the NQS.
Critical Reflection Example for Quality Area 5: Relationships with Children
Focus: Reflecting on building positive relationships with children and how it aligns with Quality Area 5.
Information Gathered:
-
Observation notes on interactions between educators and children.
-
Feedback from children, families, and colleagues regarding relationships and interactions.
-
Records of children's social and emotional development.
-
Input from children about their feelings of belonging and inclusion.
Description of the Interaction: A new child joined the class and initially showed signs of shyness and reluctance to participate in group activities. Educators made concerted efforts to support the child's transition, including one-on-one interactions, engaging the child in activities of interest, and introducing them to peers.
Analysis and Evaluation:
-
What went well: The child gradually became more comfortable and started participating in group activities. Positive, respectful relationships were established through consistent one-on-one interactions and encouragement. The child showed improved confidence and began forming friendships with peers.
-
What didn't go well: Initially, there were some challenges in understanding the child's needs and preferences. The child's shyness sometimes led to moments of withdrawal and hesitation.
-
Why did it happen: The child needed time to adjust to the new environment and develop trust with educators and peers. The initial hesitations were natural and part of the child's adjustment process.
-
How did it impact children's learning and development: Building positive relationships with educators and peers supported the child's sense of belonging and inclusion. The child's increased confidence and participation contributed to their social and emotional development.
-
What could be improved: Developing more strategies to support new children during transitions, such as creating a buddy system or providing a quiet space for children to relax and adjust at their own pace.
Link to Standards:
-
Element 5.1.1: Positive educator-to-child interactions: Educators engage meaningfully and respectfully with children, fostering secure, trusting relationships. This includes providing individual attention and responding to children's cues and needs.
-
Element 5.1.2: Dignity and rights of the child: The dignity and rights of every child are maintained. This involves respecting children's individuality and supporting their emotional well-being.
-
Element 5.2.1: Collaborative learning: Children are supported to collaborate, learn from and help each other. This includes promoting positive peer interactions and fostering a sense of community.
Plan for Improvement:
-
Immediate Steps: Implement a buddy system where new children are paired with a peer to help them adjust. Create a welcoming environment with personalized activities that cater to individual children's interests and needs.
-
Long-term Goals: Develop a comprehensive transition plan for new children, including orientation sessions, parent-educator meetings, and gradual integration into the group. Provide ongoing professional development for educators on building positive relationships and supporting children's social-emotional development.
-
Professional Development: Attend workshops on relationship-building and social-emotional learning in early childhood. Encourage educators to engage in reflective practices and share strategies for supporting children's transitions.
Review and Adjust:
-
Regularly review the effectiveness of the buddy system and transition plan through observations and feedback from children, families, and educators.
-
Reflect on the impact of relationship-building strategies and make adjustments as needed to ensure all children feel supported and included.
By critically reflecting on relationships with children, I can ensure continuous improvement in fostering positive, respectful, and inclusive interactions, aligned with Quality Area 5 of the NQS.
Critical Reflection Example for Quality Area 6: Collaborative Partnerships with Families and Communities
Focus: Reflecting on the effectiveness of collaborative partnerships with families and communities and how they align with Quality Area 6.
Information Gathered:
-
Feedback from families and community members through surveys and informal conversations.
-
Records of family and community involvement in center activities.
-
Observations of children's interactions with family members and community guests during events.
-
Notes from staff meetings discussing family and community engagement.
Description of the Partnership: The center organizes regular events and activities to engage families and the community, such as parent-teacher meetings, cultural celebrations, and community visits. Families are encouraged to participate in their children's learning and development, and community members are invited to share their expertise and resources.
Analysis and Evaluation:
-
What went well: The events and activities were well-attended by families and community members. Families felt welcomed and valued, contributing to a strong sense of community within the center. Children benefited from the diverse experiences and perspectives brought by community guests.
-
What didn't go well: Some families faced barriers to participation, such as work schedules and language differences. There were occasional miscommunications about event details and expectations.
-
Why did it happen: The barriers to participation were due to practical constraints and a lack of tailored communication strategies. Miscommunications occurred because of inconsistent information sharing.
-
How did it impact children's learning and development: The collaborative partnerships enriched children's learning by exposing them to different cultures, professions, and experiences. However, limited participation by some families meant that not all children equally benefited from these opportunities.
-
What could be improved: Developing more flexible and inclusive strategies to accommodate different family schedules and language needs. Enhancing communication channels to ensure consistent and clear information sharing.
Link to Standards:
-
Element 6.1.1: Engagement with the service: Families are supported from enrolment to be involved in the service and contribute to service decisions. This involves creating a welcoming environment and encouraging family participation.
-
Element 6.1.2: Parent views are respected: The expertise, culture, values, and beliefs of families are respected and families share in decision-making about their child's learning and wellbeing. This includes actively seeking and valuing family input.
-
Element 6.2.3: Community engagement: The service builds relationships and engages with its community. This includes inviting community members to participate in the program and fostering connections between children and the broader community.
Plan for Improvement:
-
Immediate Steps: Offer events at different times of the day and provide translations for key communications to accommodate diverse family needs. Use multiple communication channels, such as newsletters, emails, and social media, to ensure all families receive consistent information.
-
Long-term Goals: Develop a family and community engagement plan that includes regular surveys to gather feedback and identify areas for improvement. Create opportunities for families to share their culture and expertise with the center, fostering a more inclusive environment.
-
Professional Development: Attend workshops on effective family and community engagement strategies. Encourage staff to engage in reflective practices and share successful strategies for building partnerships with families and the community.
Review and Adjust:
-
Regularly review feedback from families and community members to assess the effectiveness of engagement strategies.
-
Reflect on the impact of collaborative partnerships on children's learning and development and make adjustments as needed to ensure all families and community members feel included and valued.
By critically reflecting on collaborative partnerships with families and communities, I can ensure continuous improvement in fostering strong, inclusive, and supportive relationships, aligned with Quality Area 6 of the NQS.
Critical Reflection Example for Quality Area 7: Governance and Leadership
Focus: Reflecting on the effectiveness of governance and leadership practices in fostering a culture of continuous improvement and how they align with Quality Area 7.
Information Gathered:
-
Feedback from staff, families, and community members about leadership and decision-making processes.
-
Records of staff meetings, professional development sessions, and quality improvement plans.
-
Observation notes on the implementation of policies and procedures.
-
Input from staff about their professional growth and satisfaction.
Description of the Governance and Leadership Practices: The center has a leadership team responsible for overseeing the implementation of policies and procedures, supporting staff professional development, and ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements. Regular staff meetings and professional development sessions are held to promote a culture of continuous improvement.
Analysis and Evaluation:
-
What went well: The leadership team effectively communicated the center's vision and goals, fostering a shared sense of purpose among staff. Regular professional development opportunities were provided, supporting staff growth and improving practice. Policies and procedures were consistently implemented, ensuring compliance and maintaining high standards.
-
What didn't go well: Some staff members felt that their input was not always considered in decision-making processes. There were occasional gaps in communication, leading to misunderstandings and inconsistencies in practice.
-
Why did it happen: The decision-making processes may have lacked transparency, and communication channels were not always effective. This could be due to the leadership team being overwhelmed with multiple responsibilities.
-
How did it impact children's learning and development: Effective governance and leadership practices supported a stable and high-quality learning environment for children. However, the occasional gaps in communication and decision-making processes affected staff morale and consistency in practice, potentially impacting the quality of care and education.
-
What could be improved: Enhancing transparency in decision-making processes and ensuring that all staff members feel heard and valued. Improving communication channels to facilitate clear and consistent information sharing.
Link to Standards:
-
Element 7.1.1: Service philosophy and purpose: A statement of philosophy guides all aspects of the service's operations. This involves ensuring that the service's vision, mission, and goals are clearly communicated and aligned with practices.
-
Element 7.2.1: Continuous improvement: There is an effective self-assessment and quality improvement process in place. This includes regularly reflecting on practices and implementing strategies to enhance quality.
-
Element 7.2.2: Educational leadership: The educational leader is supported and leads the development and implementation of the educational program and assessment and planning cycle. This involves providing guidance and support to educators to improve their practice.
-
Element 7.2.3: Development of professionals: Educators, co-ordinators, and staff members' performance is regularly evaluated, and individual plans are in place to support learning and development. This includes offering professional development opportunities and fostering a culture of continuous improvement.
Plan for Improvement:
-
Immediate Steps: Establish regular forums for staff to provide input and feedback on decision-making processes. Enhance communication channels, such as using digital platforms for information sharing and updates.
-
Long-term Goals: Develop a transparent decision-making framework that includes staff input and feedback. Implement regular evaluations of leadership practices to ensure they are effective and aligned with the service's vision and goals.
-
Professional Development: Organize leadership training sessions for the leadership team to enhance their skills in communication, decision-making, and team building. Encourage staff to pursue further education and training to support their professional growth.
Review and Adjust:
-
Regularly review feedback from staff, families, and community members to assess the effectiveness of governance and leadership practices.
-
Reflect on the impact of leadership practices on the quality of care and education and make adjustments as needed to ensure continuous improvement.
By critically reflecting on governance and leadership practices, I can ensure continuous improvement in fostering a culture of collaboration, transparency, and professional growth, aligned with Quality Area 7 of the NQS.
How To Organise Critical Reflections
Steps to Organize Critical Reflections
-
Set Clear Objectives:
-
Define what you want to achieve through your reflections.
-
Identify the key areas or aspects of practice you want to reflect on.
-
-
Gather Relevant Information:
-
Collect observations, feedback, and data related to the focus area.
-
Include input from children, families, and colleagues as appropriate.
-
-
Create a Reflection Template:
-
Develop a standardized template to organize your reflections. This can help ensure consistency and thoroughness. Here’s an example template:
-
-
Schedule Regular Reflection Time:
-
Set aside dedicated time for critical reflection on a regular basis (e.g., weekly, monthly).
-
Ensure you have a quiet and uninterrupted space for reflection.
-
-
Collaborate with Colleagues:
-
Share your reflections with colleagues and seek their input.
-
Engage in reflective discussions during staff meetings or professional development sessions.
-
-
Document and Store Reflections:
-
Keep a reflective journal or use digital tools to document your reflections.
-
Organize your reflections by date or topic for easy reference.
-
-
Implement and Monitor Improvement Plans:
-
Put your action plans into practice and monitor their effectiveness.
-
Collect feedback and data to evaluate the impact of your improvements.
-
-
Review and Revise:
-
Regularly review your reflections and action plans.
-
Make necessary adjustments to ensure continuous improvement.
-
Further Reading
Critical Reflections In The Assessment and Rating Process
Educators Guide To Critical Reflections
Reflection Vs Critical Reflection
Critical Reflection Questions For NQS QA1
Critical Reflection Questions For NQS QA2
How To Write A Critical Reflection In Early Childhood







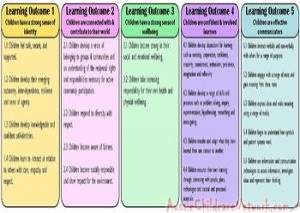 Here is the list of the EYLF Learning Outcomes that you can use as a guide or reference for your documentation and planning. The EYLF
Here is the list of the EYLF Learning Outcomes that you can use as a guide or reference for your documentation and planning. The EYLF The EYLF is a guide which consists of Principles, Practices and 5 main Learning Outcomes along with each of their sub outcomes, based on identity,
The EYLF is a guide which consists of Principles, Practices and 5 main Learning Outcomes along with each of their sub outcomes, based on identity, This is a guide on How to Write a Learning Story. It provides information on What Is A Learning Story, Writing A Learning Story, Sample
This is a guide on How to Write a Learning Story. It provides information on What Is A Learning Story, Writing A Learning Story, Sample One of the most important types of documentation methods that educators needs to be familiar with are “observations”. Observations are crucial for all early childhood
One of the most important types of documentation methods that educators needs to be familiar with are “observations”. Observations are crucial for all early childhood To support children achieve learning outcomes from the EYLF Framework, the following list gives educators examples of how to promote children's learning in each individual
To support children achieve learning outcomes from the EYLF Framework, the following list gives educators examples of how to promote children's learning in each individual Reflective practice is learning from everyday situations and issues and concerns that arise which form part of our daily routine while working in an early
Reflective practice is learning from everyday situations and issues and concerns that arise which form part of our daily routine while working in an early Within Australia, Programming and Planning is reflected and supported by the Early Years Learning Framework. Educators within early childhood settings, use the EYLF to guide
Within Australia, Programming and Planning is reflected and supported by the Early Years Learning Framework. Educators within early childhood settings, use the EYLF to guide When observing children, it's important that we use a range of different observation methods from running records, learning stories to photographs and work samples. Using
When observing children, it's important that we use a range of different observation methods from running records, learning stories to photographs and work samples. Using This is a guide for educators on what to observe under each sub learning outcome from the EYLF Framework, when a child is engaged in
This is a guide for educators on what to observe under each sub learning outcome from the EYLF Framework, when a child is engaged in The Early Years Learning Framework describes the curriculum as “all the interactions, experiences, activities, routines and events, planned and unplanned, that occur in an environment
The Early Years Learning Framework describes the curriculum as “all the interactions, experiences, activities, routines and events, planned and unplanned, that occur in an environment


