Importance of Critical Reflections
-
Self-Assessment: Critical reflections allow educators to assess their own practices, identify strengths and weaknesses, and make informed decisions about how to improve their teaching and learning strategies.
-
Evidence of Quality: Reflective practices provide evidence of an educator's commitment to high-quality education and care. They demonstrate that educators are actively engaged in evaluating and enhancing their practices.
-
Continuous Improvement: Through critical reflections, educators can identify areas for growth and set goals for professional development. This continuous improvement process is essential for maintaining high standards in early childhood education.
-
Informed Planning: Reflective practices help educators make informed decisions about curriculum planning, teaching strategies, and interactions with children. This leads to more effective and responsive educational programs.
How to Incorporate Critical Reflections in the Assessment and Rating Process
-
Documenting Reflections: Keep a reflective journal or use digital tools to document your reflections regularly. Record significant events, interactions, and observations, and analyze them critically.
-
Linking to Standards: Relate your reflections to the National Quality Standard (NQS) and other relevant frameworks. Highlight how your practices align with the quality areas and elements outlined in the NQS.
-
Collaborative Reflections: Engage in collaborative reflections with colleagues. Share your insights, discuss challenges, and brainstorm solutions together. This collaborative approach can enhance the quality of reflections.
-
Professional Development: Use your reflections to identify areas for professional development. Participate in workshops, courses, and training sessions to build your skills and knowledge.
-
Action Plans: Develop action plans based on your reflections. Set specific, achievable goals and outline the steps you will take to implement changes. Monitor your progress and adjust your plans as needed.
-
Feedback and Evaluation: Seek feedback from colleagues, supervisors, and families. Use this feedback to inform your reflections and make continuous improvements.
Example Reflection
Focus: Reflecting on a challenging interaction with a child displaying aggressive behavior.
Description: During playtime, a child named Sam pushed another child and took their toy. Despite my efforts to intervene and calm Sam, the aggressive behavior continued.
Analysis: I felt frustrated and unsure of how to effectively manage the situation. My initial response was to separate the children and explain the importance of sharing, but this approach did not resolve the issue.
Connection to Theory: According to social-emotional learning theories, children may display aggressive behavior when they lack the skills to regulate their emotions and communicate their needs. Sam's behavior may have been a result of frustration or unmet needs.
Improvement: I need to develop more effective strategies for supporting children with challenging behaviors. This includes understanding the underlying causes of the behavior and teaching alternative ways to express emotions.
Action Plan:
-
Training: Attend a workshop on managing challenging behaviors and social-emotional learning.
-
Strategies: Implement strategies such as emotion coaching, problem-solving activities, and positive reinforcement.
-
Communication: Collaborate with Sam's parents to understand his needs and develop consistent approaches between home and school.
Conclusion: This reflection highlighted the need for additional training and strategies to support children with challenging behaviors. By implementing the action plan, I aim to create a more positive and supportive environment for all children.
Topics For Critical Reflection In The Assessment And Rating Process
Critical reflection is an essential part of the assessment and rating process in early childhood education. Here are some key topics to consider:
1. Educational Program and Practice
-
How are the children's interests and developmental needs incorporated into the program?
-
What strategies are used to encourage active learning and engagement?
-
How is intentional teaching implemented in daily activities?
2. Children's Health and Safety
-
How are health and safety policies implemented and monitored?
-
What measures are taken to create a safe and healthy environment for children?
-
How is hygiene and illness prevention managed?
3. Physical Environment
-
How does the physical environment support and extend children’s learning?
-
What adaptations are made to accommodate the needs of all children?
-
How is sustainability incorporated into the daily operations?
4. Staffing Arrangements
-
How are educators supported in their professional development?
-
What strategies are in place to ensure effective teamwork and communication?
-
How is staff performance monitored and improved?
5. Relationships with Children
-
How are positive relationships with children fostered?
-
What techniques are used to support children’s social and emotional development?
-
How is behavior guidance managed and supported?
6. Collaborative Partnerships with Families and Communities
-
How are families involved in the decision-making process?
-
What strategies are used to build strong partnerships with families?
-
How is community involvement encouraged and maintained?
7. Leadership and Service Management
-
How is leadership demonstrated and shared within the service?
-
What processes are in place for continuous improvement?
-
How are policies and procedures evaluated and updated?
By reflecting on these areas, educators can gain insights into their practices and identify opportunities for improvement.
Further Reading
Educators Guide To Critical Reflections
Reflection Vs Critical Reflection
Critical Reflection Questions For NQS QA1
Critical Reflection Questions For NQS QA2
How To Write A Critical Reflection In Early Childhood







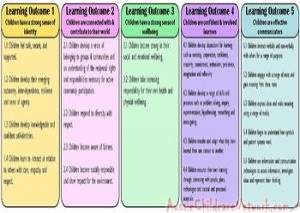 Here is the list of the EYLF Learning Outcomes that you can use as a guide or reference for your documentation and planning. The EYLF
Here is the list of the EYLF Learning Outcomes that you can use as a guide or reference for your documentation and planning. The EYLF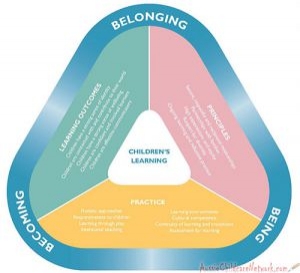 The EYLF is a guide which consists of Principles, Practices and 5 main Learning Outcomes along with each of their sub outcomes, based on identity,
The EYLF is a guide which consists of Principles, Practices and 5 main Learning Outcomes along with each of their sub outcomes, based on identity, This is a guide on How to Write a Learning Story. It provides information on What Is A Learning Story, Writing A Learning Story, Sample
This is a guide on How to Write a Learning Story. It provides information on What Is A Learning Story, Writing A Learning Story, Sample One of the most important types of documentation methods that educators needs to be familiar with are “observations”. Observations are crucial for all early childhood
One of the most important types of documentation methods that educators needs to be familiar with are “observations”. Observations are crucial for all early childhood To support children achieve learning outcomes from the EYLF Framework, the following list gives educators examples of how to promote children's learning in each individual
To support children achieve learning outcomes from the EYLF Framework, the following list gives educators examples of how to promote children's learning in each individual Reflective practice is learning from everyday situations and issues and concerns that arise which form part of our daily routine while working in an early
Reflective practice is learning from everyday situations and issues and concerns that arise which form part of our daily routine while working in an early Within Australia, Programming and Planning is reflected and supported by the Early Years Learning Framework. Educators within early childhood settings, use the EYLF to guide
Within Australia, Programming and Planning is reflected and supported by the Early Years Learning Framework. Educators within early childhood settings, use the EYLF to guide When observing children, it's important that we use a range of different observation methods from running records, learning stories to photographs and work samples. Using
When observing children, it's important that we use a range of different observation methods from running records, learning stories to photographs and work samples. Using This is a guide for educators on what to observe under each sub learning outcome from the EYLF Framework, when a child is engaged in
This is a guide for educators on what to observe under each sub learning outcome from the EYLF Framework, when a child is engaged in The Early Years Learning Framework describes the curriculum as “all the interactions, experiences, activities, routines and events, planned and unplanned, that occur in an environment
The Early Years Learning Framework describes the curriculum as “all the interactions, experiences, activities, routines and events, planned and unplanned, that occur in an environment


