This is a guide for educators on what to observe under each sub learning outcome from the MTOP Framework, when a child is engaged in play and learning. Educators can plan experiences for the curriculum and gain an understanding on how children can achieve each individual outcome.
Learning Outcome 1: Children have a strong sense of identity
1.1 - Children feel safe, secure, and supported
This is evident when children:
- establish and maintain respectful, trusting relationships with other children and educators
- use effective routines to make predicted transitions
- sense and respond to a feeling of belonging
- openly express their feelings and ideas in their interactions with others
- respond to ideas and suggestions from others
- initiate interactions and conversations with trusted educators
- confidently explore and engage with social and physical environments through relationships and play
- initiate and join in play and leisure activitie
1.2 - Children develop their autonomy, inter-dependence, resilience and sense of agency
This is evident when children:
- participate in a range of freely chosen play and leisure opportunities
- demonstrate awareness of the needs and rights of others
- are open to new challenges and discoveries
- demonstrate awareness of the opinions of others about their efforts
- increasingly co-operate and work collaboratively with others
- take considered risk in their decision-making and cope with the unexpected
- recognise their individual achievements and the achievements of others
- demonstrate a capacity for self-regulation, negotiating and sharing behaviours
- persist when faced with challenges and when first attempts are not successful
- display a willingness to achieve to the best of one’s ability
1.3 Children develop knowledgeable and confident self identities
This is evident when children:
- feel recognised and respected for who they are
- explore different identities and points of view in play and discussions
- develop a wider sense of the diverse values and beliefs held by others
- share aspects of their culture with the other children and educators
- use their home language to construct meaning
- develop strong foundations in both the culture and language/s of their family and of the broader community without compromising their cultural identities
- develop their social and cultural heritage through engagement with Elders and community members
- reach out and communicate for comfort, assistance and companionship
- celebrate and share their contributions and achievements with others
1.4 Children learn to interact in relation to others with care, empathy and respect
This is evident when children:
- show interest in other children and being part of a group
- spend a large proportion of their time with peers
- establish and maintain relationships with peers
- engage in and contribute to play and leisure experiences
- express a wide range of emotions, thoughts and views constructively
- empathise with and express concern for others
- display awareness of and respect for others’ perspectives
- reflect on their actions and consider consequences for others
- learn to control strong emotions and impulses
Learning Outcome 2: Children Are Connected With and Contribute To Their World
2.1 Children develop a sense of belonging to groups and communities and an understanding of the reciprocal rights and responsibilities necessary for active community participation
This is evident when children:
- recognise that they have a right to belong to many communities
- cooperate with others and negotiate roles and relationships in play and leisure experiences
- take action to assist other children to participate in social groups
- broaden their understanding of the world in which they live
- express an opinion in matters that affect them
- build on their own social experiences to explore other ways of being
- learn to ‘read’ the behaviours of others and respond appropriately
- understand different ways of contributing through play and meaningful projects
- respond positively to others, reaching out for company and friendship
- contribute to fair decision-making about matters that affect them
2.2 Children respond to diversity with respect
This is evident when children:
- use opportunities to develop understandings
- about the diversity of culture, heritage,
- background and tradition
- demonstrate awareness of connections, similarities and differences between people and react in positive ways
- listen to others’ ideas and respect different ways of being and doing
- practise inclusive ways of achieving coexistence
2.3 Children become aware of fairness
This is evident when children:
- become aware of ways in which people are included or excluded from physical and social environments
- develop the ability to recognise unfairness and bias and the capacity to act with compassion and kindness
- are empowered to make choices and problem solve to meet their needs in particular contexts
- think critically about fair and unfair behaviour
- understand and evaluate ways in which texts and media construct identities and reate stereotypes
2.4 Children become socially responsible and show respect for the environment
This is evident when children:
- demonstrate an increasing knowledge of, and respect for natural and constructed environments
- demonstrate an awareness of the impact of human activity on environments and the interdependence of living things
- participate with others to solve problems and contribute to group outcomes
- explore, infer, predict and hypothesise in order to develop an increased understanding of the interdependence between land, people, plants and animals
- show appreciation and care for natural and constructed environments
- act with moral and ethical integrity
- appreciate social, cultural, linguistic and religious diversity
Learning Outcome 3: Children have a strong sense of wellbeing
3.1 Children become strong in their social and emotional wellbeing
This is evident when children:
- demonstrate trust and confidence
- share humour, happiness and satisfaction
- celebrate their own efforts and achievements and those of others
- increasingly co-operate and work collaboratively with others
- enjoy moments of solitude
- make choices, accept challenges, take considered risks, manage change and cope with frustrations
- show self-regulation and manage their emotions in ways that reflect the feelings and needs of others
- use moral reasoning to solve problems
- assert their capabilities and independence while demonstrating increasing awareness of the needs and rights of others
- recognise the contributions they make to shared projects and experiences and anticipate realistic consequences
3.2 Children take increasing responsibility for their own health and physical wellbeing
This is evident when children:
- are happy, healthy, safe and connected to others
- regulate their emotions by concentrating, focussing and calming
- combine gross and fine motor movement and balance to achieve complex patterns of activity including dance, creative movement, drama, and sports
- manipulate equipment and manage tools with increasing competence and skill
- show an increasing awareness of healthy lifestyles and good nutrition
- show enthusiasm for participating in physical play
- negotiate environments to ensure the safety and wellbeing of themselves and others
- seek out positive experiences
Learning Outcome 4: Children are confident and involved learners
4.1 Children develop dispositions such as curiosity, cooperation, confidence, creativity, commitment,enthusiasm, persistence, imagination and reflexivity
This is evident when children:
- freely follow and extend their own interests with enthusiasm, curiosity, energy and concentration
- investigate, imagine and explore ideas
- initiate and contribute to play and leisure experiences emerging from their own ideas
- participate in a variety of rich and meaningful inquiry-based experiences
- persevere even when they find a task difficult and experience the satisfaction of achievement
4.2 Children use a range of skills and processes such as problem solving, enquiry, experimentation, hypothesising, researching and investigating
This is evident when children:
- apply a wide variety of thinking strategies to engage with situations and solve problems, and adapt these strategies to new situations
- create and use representation to organise, record and communicate ideas and concepts
- make predictions and generalisations about their daily activities, aspects of the natural world and environments
- manipulate objects and experiment with cause and effect through trial and error
- use reflective thinking to consider why things happen and what can be learnt from these experiences
- show leadership, and follow directions given by other children
- make choices and take control
4.3 Children transfer and adapt what they have learned from one context to another
This is evident when children:
- make connections between experiences,
- concepts and processes
- use the processes of play, reflection and investigation to solve problems
- try out strategies that were effective to solve problems in one situation in a new context
4.4 Children resource their own learning through connecting with people, place, technologies and natural and processed materials
This is evident when children:
- experience the benefits and pleasures of shared exploration of new ideas
- explore the purpose and function of a range of tools, media,
- manipulate resources to investigate, take apart, assemble, invent and construct
- experiment with and use information and communication technologies (ICT) to investigate and problem solve
- explore ideas and theories using imagination and creativity
- use feedback from themselves and others to revise and build on an idea
Learning Outcome 5 - Children are effective communicators
5.1 Children interact verbally and non-verbally with others for a range of purposes
This is evident when children:
- engage in enjoyable interactions using verbal and non-verbal language
- convey and construct messages with purpose and confidence, building on home/family and community literacies
- use language and representations from play, music and art to share and project meaning
- contribute their ideas and experiences in play, small and large group discussions, including decision-making opportunities such as making group rules
- are independent communicators who initiate Standard Australian English and home language conversations and demonstrate the ability to meet the listeners’ needs
- interact with others to explore ideas and concepts, clarify and challenge thinking, debate, negotiate and share new understandings
- convey and construct messages with purpose and confidence, for example expressing needs, conflict resolution, following directions
- express ideas and feelings and understand and respect the perspectives of others
- use verbal and non-verbal language to communicate thinking
- participate in play opportunities that promote social interaction with peers
5.2 Children engage with a range of texts and gain meaning from these texts
This is evident when children:
- enjoy stories, verse and lyrics
- view, listen to and enjoy printed, visual and multimedia texts
- take on roles of literacy and numeracy users in their play
- actively use, engage with and share the enjoyment of language and texts in a range of ways
- recognise and engage with written and oral culturally constructed texts
- use a range of texts for instructions for leisure activities such as sport and craft
5.3 Children collaborate with others, express ideas and make meaning using a range of media and communication technologies
This is evident when children:
- engage with media and technology for fun and to make meaning
- use language and engage in play to imagine and create roles, scripts and ideas
- use the creative arts such as drawing, painting, sculpture, drama, dance, movement, music and storytelling
- use technologies in everyday life, for example recording daily activities in program journals
- use information and communication technologies to express ideas, access images, information and explore diverse perspectives
- engage with information and communication technology tools for designing, drawing, editing,reflecting and composing







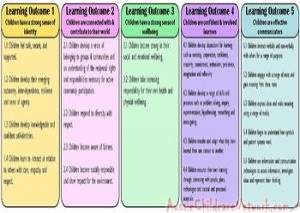 Here is the list of the EYLF Learning Outcomes that you can use as a guide or reference for your documentation and planning. The EYLF
Here is the list of the EYLF Learning Outcomes that you can use as a guide or reference for your documentation and planning. The EYLF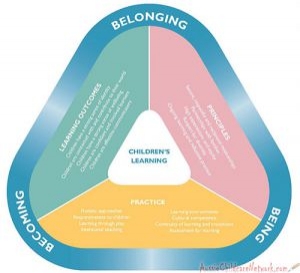 The EYLF is a guide which consists of Principles, Practices and 5 main Learning Outcomes along with each of their sub outcomes, based on identity,
The EYLF is a guide which consists of Principles, Practices and 5 main Learning Outcomes along with each of their sub outcomes, based on identity, This is a guide on How to Write a Learning Story. It provides information on What Is A Learning Story, Writing A Learning Story, Sample
This is a guide on How to Write a Learning Story. It provides information on What Is A Learning Story, Writing A Learning Story, Sample One of the most important types of documentation methods that educators needs to be familiar with are “observations”. Observations are crucial for all early childhood
One of the most important types of documentation methods that educators needs to be familiar with are “observations”. Observations are crucial for all early childhood To support children achieve learning outcomes from the EYLF Framework, the following list gives educators examples of how to promote children's learning in each individual
To support children achieve learning outcomes from the EYLF Framework, the following list gives educators examples of how to promote children's learning in each individual Reflective practice is learning from everyday situations and issues and concerns that arise which form part of our daily routine while working in an early
Reflective practice is learning from everyday situations and issues and concerns that arise which form part of our daily routine while working in an early Within Australia, Programming and Planning is reflected and supported by the Early Years Learning Framework. Educators within early childhood settings, use the EYLF to guide
Within Australia, Programming and Planning is reflected and supported by the Early Years Learning Framework. Educators within early childhood settings, use the EYLF to guide When observing children, it's important that we use a range of different observation methods from running records, learning stories to photographs and work samples. Using
When observing children, it's important that we use a range of different observation methods from running records, learning stories to photographs and work samples. Using This is a guide for educators on what to observe under each sub learning outcome from the EYLF Framework, when a child is engaged in
This is a guide for educators on what to observe under each sub learning outcome from the EYLF Framework, when a child is engaged in The Early Years Learning Framework describes the curriculum as “all the interactions, experiences, activities, routines and events, planned and unplanned, that occur in an environment
The Early Years Learning Framework describes the curriculum as “all the interactions, experiences, activities, routines and events, planned and unplanned, that occur in an environment


