Knowledge, Skills and Dispositions describe how children explore during the Kindergarten Year within a holistic learning program.
In addition, teachers work with family, community and other partners to negotiate learning and development priorities. Teachers use Knowledge, Skills and dispositions to plan opportunities to engage children in integrated learning through play, real-life engagements, routines and transitions.
Identity
1.1 Building a sense of security and trust.
Teachers promote the following aspects of children’s learning:
- a sense of emotional safety in familiar environments
- confidence that familiar people will provide support in times of need or change
- feelings of acceptance for who they are by family, educators and peers
- a sense of stability and dependability in relationships with a variety of familiar people (family, educators and peers) in familiar environments
- a sense of belonging to their family, community and kindergarten community
- enjoyment and satisfaction as they explore the indoor and outdoor play environments
- enjoyment and satisfaction when engaging in play and learning with peers and familiar adults.
1.2 Acting with increasing independence and perseverance.
Teachers promote the following aspects of children’s learning:
- the ability to organise and manage needs and activities
- the ability to manage classroom routines and processes
- the ability to organise people and resources in order to engage in a variety of play situations
- the ability to make choices
- self-organisation of personal belongings
- self-organisation of resources and materials for play
- perseverance when trying new and challenging tasks.
1.3 Building a confident self-identity.
Teachers promote the following aspects of children’s learning:
- pride and confidence in “who they are” as a member of their family, community and place, that is, their environment
- pride and confidence in “who they are” and “where they come from” including their languages, cultural identity and heritage
- pride and confidence in “who they are” as a member of the learning community
- pride and confidence in their abilities, preferences and achievements
- confidence to explore the environment and engage in a variety of types of play and learning experiences
- confidence when approaching tasks, people and situations
- confidence to share experiences, feelings and ideas
- confidence to try new and challenging tasks
- confidence to make choices and take considered risks.
Connectedness
2.1 Building positive relationships with others.
Teachers promote the following aspects of children’s learning:
- pride in their connections to familiar places, people, groups, language, communities, culture, shared pasts and futures
- ways to connect and engage with a variety of peers and people
- social skills for initiating interactions and contributing to play
- skills for cooperating (including sharing and turn-taking) and collaborating
- skills for resolving conflicts and problem solving in social contexts
- active engagement in group learning situations
- awareness of the reciprocal nature of rights and responsibilities
- positive ways to respond to others’ efforts to interact, e.g. answering a friend’s question, helping someone to join in, smiling and nodding to show you are interested
- desire to help others enjoy, join in, achieve their goals and manage tasks or situations
- awareness of fair and unfair behaviours in everyday situations
2.2 Showing increasing respect for diversity.
Teachers promote the following aspects of children’s learning:
- awareness of their own culture, e.g. language, practices, connections to people and place/s or country, heritage
- awareness of other cultures, e.g. languages, practices, connections to people and place/s or country, heritages
- understandings about Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander cultures and their strong connection to place, language, histories and community
- active engagement with a range of people, groups and communities
- beginning appreciation of various aspects of diversity, including family structures, roles in
- communities, religions, practices, capabilities, talents and locations, e.g. urban, rural or remote
- ways to respect and value similarities and differences in people’s feelings, needs, ideas and opinions
- ways to respond positively and show respect for diverse viewpoints, cultures, heritages, backgrounds, traditions, languages and ways of knowing and being
- early understandings about and willingness to question bias and stereotypes in play and everyday situations.
2.3 Showing increasing respect for environments.
Teachers promote the following aspects of children’s learning:
- interest in natural, built and technological environments and change in these environments
- ways to care for and respect the people, objects and spaces in their home, community and kindergarten environments
- interest in ways to care for and respect plants and animals
- interest in the relationships among people, land, plants and animals
- awareness of positive and negative interactions between humans and environments
- awareness of ways to help sustain familiar environments
- awareness and valuing of Australia’s environmental heritage.
Wellbeing
3.1 Building a sense of autonomy and wellbeing.
Teachers promote the following aspects of children’s learning:
- a sense of being able to make decisions and choices and willingness to do so (sense of agency)
- understandings about and ability to express their feelings
- participation in arts and aesthetic experiences as a form of self-expression and a way to celebrate
- strategies for self-regulating feelings and responses to people and situations
- enjoyment of solitude, quietness, reflection and relaxation
- a sense of being able to manage challenges, participate in new interactions and routines and try new experiences
- strategies for managing change and unexpected situations or occurrences and dealing with disappointments (resilience).
3.2 Exploring ways to show care and concern and interact positively with others.
Teachers promote the following aspects of children’s learning:
- ways to show consideration and concern for others’ feelings and needs
- ways to show empathy, help and care for others
- an awareness of others’ interests, feelings and needs
- ways to enjoy and have fun with others
- interest in interacting with others in a variety of play, real-life, routine and group situations
- ways to relate positively with others, be a companion and behave in a friendly way
- ways to recognise and celebrate children’s contributions
- ways to accept and give affirmations.
3.3 Exploring ways to promote own and others health and safety.
Teachers promote the following aspects of children’s learning:
- ways to keep themselves and others healthy, e.g. eating healthy foods, resting, choosing healthy activities, using a tissue to blow their nose, covering sneezes or coughs
- increasing independence in managing personal hygiene and self-care routines
- ways to keep themselves and others safe, e.g. following rules, looking and thinking before jumping, swinging or running.
3.4 Exploring ways to promote physical wellbeing.
Teachers promote the following aspects of children’s learning:
- confidence in developing movement skills and managing movement challenges
- sensory skills and awareness, perceptual motor skills, kinaesthetic and spatial awareness, balance, coordination, muscle tone, strength and flexibility
- fine-motor skills, including: – manipulating tools and objects with control, visual tracking in purposeful contexts, e.g. using scissors to cut collage materials, experimenting with drawing tools, manipulative and construction equipment – visual tracking in purposeful contexts, e.g. following a moving object, or tracking across an image with the eyes
- fundamental movement skills, including balancing, crawling, running, jumping, catching, hopping, throwing, galloping, skipping, leaping, kicking, striking and dodging
- non-locomotor skills, e.g. swaying, turning, twisting
- hand–eye, foot–eye coordination and ball skills
Active Learning
4.1 Building positive dispositions and approaches towards learning.
Teachers promote the following aspects of children’s learning:
- curiosity and wonder, creativity, enthusiasm, drive and motivation to learn
- awareness of their successes, useful strategies, skills for learning and when to use these in particular learning situations
- capabilities required to make informed choices, plan and carry out plans
- ways to find out, research, investigate, inquire and solve problems
- thinking, including inferring, predicting, hypothesising, testing, experimenting, evaluating and generalising
- active investigation of scientific ideas, processes and language in everyday life
- exploration of relationships, including cause–effect, e.g. “What caused the sand castle to collapse?”, “What happened when you made the ramp higher?”
- active investigation of mathematical ideas, processes and language in everyday life related to shape and to comparing, changing, measuring and recording quantities
- awareness that they can learn by copying others, repeating and practising actions, behaviours and language
- strategies for making links between ideas and experiences and applying learning to new situations
- reflection by talking about and using feedback about thinking and learning.
4.2 Increasing confidence and involvement in learning.
Teachers promote the following aspects of children’s learning:
- the ability to focus on important aspects of learning situations and sustain concentration
- confidence to actively engage in and contribute to a range of learning situations and investigations
- ways to plan, think about and organise resources needed for self-chosen learning (materials, space or people)
- ways to contribute to learning conversations
- ways to sustain involvement in play and learning
- confidence to become involved in learning conversations
4.3 Engaging in ways to be imaginative and creative.
Teachers promote the following aspects of children’s learning:
- imagination and experimentation with possibilities
- appreciation of various ways of engaging with ideas, materials, processes and a range of media
- sensory exploration of the world, objects and materials indoors and outdoors
- the ability to generate ideas and solutions, innovate and invent
- exploration of and interest in multiple ways to create and represent with a variety of media materials, tools and processes
- exploration of and interest in multiple ways to create and represent visually, using sound, movement and language
- exploration of and interest in arts elements and principles and their use when creating and representing ideas, feelings and experiences
- exploration of and interest in representing and creating through imaginative, fantasy, symbolic and dramatic play
- exploration of and interest in cultural, traditional and contemporary music, visual arts, dance, drama and media
- engagement with ways to create and represent using ICTs and various media.
4.4 Exploring tools technologies and information and communication technologies (ICTs).
- Teachers promote the following aspects of children’s learning:
- interest in and understandings about everyday tools, e.g. utensils, pencils, hammers, levers, cogs, wheels, pumps, musical instruments, fishing tools
- interest in and understandings about everyday technologies, e.g. kitchen machines, audio/video devices, scales, scanners, mobile phones, digital cameras
- interest in and understandings about existing and emerging ICTs
- interest in sharing personal and cultural experiences with technologies and exploring emerging technologies
- skills and confidence to use a wide variety of tools, technologies and ICTs for a range of purposes, e.g. to support play, for enjoyment, to create, find out, communicate, share ideas and learning, inquire, investigate and solve problems.
Reference:
State Government Of Queensland (2010), Queensland Kindergarten Learning Guidelines







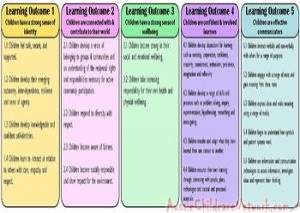 Here is the list of the EYLF Learning Outcomes that you can use as a guide or reference for your documentation and planning. The EYLF
Here is the list of the EYLF Learning Outcomes that you can use as a guide or reference for your documentation and planning. The EYLF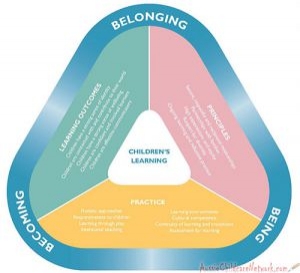 The EYLF is a guide which consists of Principles, Practices and 5 main Learning Outcomes along with each of their sub outcomes, based on identity,
The EYLF is a guide which consists of Principles, Practices and 5 main Learning Outcomes along with each of their sub outcomes, based on identity, This is a guide on How to Write a Learning Story. It provides information on What Is A Learning Story, Writing A Learning Story, Sample
This is a guide on How to Write a Learning Story. It provides information on What Is A Learning Story, Writing A Learning Story, Sample One of the most important types of documentation methods that educators needs to be familiar with are “observations”. Observations are crucial for all early childhood
One of the most important types of documentation methods that educators needs to be familiar with are “observations”. Observations are crucial for all early childhood To support children achieve learning outcomes from the EYLF Framework, the following list gives educators examples of how to promote children's learning in each individual
To support children achieve learning outcomes from the EYLF Framework, the following list gives educators examples of how to promote children's learning in each individual Reflective practice is learning from everyday situations and issues and concerns that arise which form part of our daily routine while working in an early
Reflective practice is learning from everyday situations and issues and concerns that arise which form part of our daily routine while working in an early Within Australia, Programming and Planning is reflected and supported by the Early Years Learning Framework. Educators within early childhood settings, use the EYLF to guide
Within Australia, Programming and Planning is reflected and supported by the Early Years Learning Framework. Educators within early childhood settings, use the EYLF to guide When observing children, it's important that we use a range of different observation methods from running records, learning stories to photographs and work samples. Using
When observing children, it's important that we use a range of different observation methods from running records, learning stories to photographs and work samples. Using This is a guide for educators on what to observe under each sub learning outcome from the EYLF Framework, when a child is engaged in
This is a guide for educators on what to observe under each sub learning outcome from the EYLF Framework, when a child is engaged in The Early Years Learning Framework describes the curriculum as “all the interactions, experiences, activities, routines and events, planned and unplanned, that occur in an environment
The Early Years Learning Framework describes the curriculum as “all the interactions, experiences, activities, routines and events, planned and unplanned, that occur in an environment


