Quality Area 2 of the National Quality Standard focuses on Children’s Health and Safety, ensuring that environments are safe, hygienic, and supportive of children's well-being. Here are some practical examples of how this can be implemented in the workplace.
1. Wellbeing and Comfort (Element 2.1.1)
-
Ensuring children have appropriate opportunities for rest, sleep, and relaxation.
-
Example: Providing quiet spaces with soft cushions for children who need downtime.
2. Health Practices and Procedures (Element 2.1.2)
-
Implementing effective illness and injury management and hygiene practices.
-
Example: Regular handwashing routines and sanitization stations to prevent infections.
3. Healthy Lifestyle (Element 2.1.3)
-
Promoting healthy eating and physical activity.
-
Example: Offering nutritious meal plans and organizing outdoor play sessions to encourage movement.
4. Supervision (Element 2.2.1)
-
Ensuring children are adequately supervised at all times.
-
Example: Educators positioning themselves strategically to monitor all areas of the play space.
5. Incident and Emergency Management (Element 2.2.2)
-
Developing and practicing emergency response plans.
-
Example: Conducting fire drills and ensuring all staff are trained in first aid.
6. Child Protection (Element 2.2.3)
-
Educators understanding their roles and responsibilities in identifying and responding to children at risk.
-
Example: Providing child protection training and maintaining confidential reporting procedures.
How Can I Evaluate These Practices
Evaluating Quality Area 2 practices in your setting involves assessing health, safety, and well-being measures to ensure they meet the NQS. Here are some key strategies:
1. Self-Assessment and Reflection
-
Regularly review policies and procedures related to children’s health and safety.
-
Example: Use a risk assessment checklist to identify potential hazards in the environment.
2. Observations and Documentation
-
Track how well health and safety practices are implemented.
-
Example: Maintain incident reports and hygiene logs to monitor compliance.
3. Feedback from Families and Children
-
Gather input from families and children about health and safety measures.
-
Example: Conduct parent surveys on meal plans, hygiene routines, and emergency preparedness.
4. Peer and Mentor Reviews
-
Collaborate with colleagues to evaluate and improve safety practices.
-
Example: Organize peer observations where educators assess supervision strategies.
5. Alignment with Regulations and Standards
-
Ensure compliance with national health and safety guidelines.
-
Example: Cross-check policies with ACECQA’s Quality Area 2 standards.
6. Quality Improvement Plan (QIP)
-
Develop and update a QIP to track progress and set goals for continuous improvement.
-
Example: Identify areas for enhancement and implement action plans to address them.
Further Reading
How To Achieve Quality Area 2
Reflection Questions For Quality Area 2
Exceeding Guidance For Quality Area 2
Documentation Services Require To Support Quality Area 2
Key Terms From Quality Area 2
Understanding Quality Areas







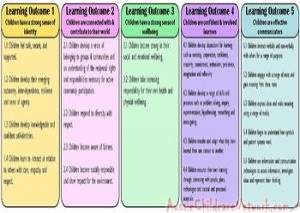 Here is the list of the EYLF Learning Outcomes that you can use as a guide or reference for your documentation and planning. The EYLF
Here is the list of the EYLF Learning Outcomes that you can use as a guide or reference for your documentation and planning. The EYLF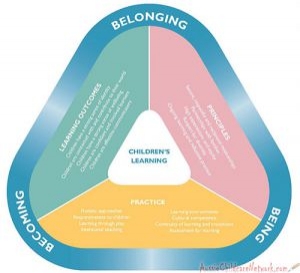 The EYLF is a guide which consists of Principles, Practices and 5 main Learning Outcomes along with each of their sub outcomes, based on identity,
The EYLF is a guide which consists of Principles, Practices and 5 main Learning Outcomes along with each of their sub outcomes, based on identity, This is a guide on How to Write a Learning Story. It provides information on What Is A Learning Story, Writing A Learning Story, Sample
This is a guide on How to Write a Learning Story. It provides information on What Is A Learning Story, Writing A Learning Story, Sample One of the most important types of documentation methods that educators needs to be familiar with are “observations”. Observations are crucial for all early childhood
One of the most important types of documentation methods that educators needs to be familiar with are “observations”. Observations are crucial for all early childhood To support children achieve learning outcomes from the EYLF Framework, the following list gives educators examples of how to promote children's learning in each individual
To support children achieve learning outcomes from the EYLF Framework, the following list gives educators examples of how to promote children's learning in each individual Reflective practice is learning from everyday situations and issues and concerns that arise which form part of our daily routine while working in an early
Reflective practice is learning from everyday situations and issues and concerns that arise which form part of our daily routine while working in an early Within Australia, Programming and Planning is reflected and supported by the Early Years Learning Framework. Educators within early childhood settings, use the EYLF to guide
Within Australia, Programming and Planning is reflected and supported by the Early Years Learning Framework. Educators within early childhood settings, use the EYLF to guide When observing children, it's important that we use a range of different observation methods from running records, learning stories to photographs and work samples. Using
When observing children, it's important that we use a range of different observation methods from running records, learning stories to photographs and work samples. Using This is a guide for educators on what to observe under each sub learning outcome from the EYLF Framework, when a child is engaged in
This is a guide for educators on what to observe under each sub learning outcome from the EYLF Framework, when a child is engaged in The Early Years Learning Framework describes the curriculum as “all the interactions, experiences, activities, routines and events, planned and unplanned, that occur in an environment
The Early Years Learning Framework describes the curriculum as “all the interactions, experiences, activities, routines and events, planned and unplanned, that occur in an environment


