Quality Area 1 of the National Quality Standard focuses on Educational Program and Practice, ensuring that learning experiences are child-centered, stimulating, and engaging. Here are some practical examples of how this can be implemented in the workplace.
-
Intentional Teaching (Element 1.2.1)
- Educators use purposeful strategies to extend children's learning.
- Example: Encouraging children to explore musical rhythms or visual arts through guided activities.
-
Child-Centered Learning (Element 1.1.2)
- Programs are designed based on children's interests, strengths, and cultural backgrounds.
- Example: Incorporating home languages into literacy-rich environments to support diverse learners.
-
Responsive Teaching and Scaffolding (Element 1.2.2)
- Educators engage in meaningful interactions to support children's development.
- Example: Using open-ended questions to encourage problem-solving and critical thinking.
-
Assessment and Planning Cycle (Element 1.3.1)
- Continuous observation and reflection guide curriculum decisions.
- Example: Documenting children's progress and planning individualized learning goals.
-
Community Connection (Element 1.1.1)
- Learning experiences reflect real-world contexts and community engagement.
- Example: Organizing nature-based explorations to teach environmental awareness.
How Can I Evaluate These Practices
Evaluating Quality Area 1 practices in your setting involves reflection, observation, and documentation to ensure that educational programs are child-centered, engaging, and effective. Here are some key strategies:
-
Self-Assessment and Reflection
- Regularly review how well your program aligns with the NQS.
- Example: Use critical reflection journals to assess the effectiveness of teaching strategies.
-
Observations and Documentation
- Track children's engagement and learning progress through observations and portfolios.
- Example: Maintain learning stories that document children's experiences and development.
-
Feedback from Families and Children
- Gather input from families and children to ensure the program meets their needs.
- Example: Conduct parent surveys or child-led discussions about their learning experiences.
-
Peer and Mentor Reviews
- Collaborate with colleagues to evaluate and improve teaching practices.
- Example: Organise peer observations where educators provide constructive feedback.
-
Alignment with Approved Learning Frameworks
- Ensure that your curriculum follows recognized learning frameworks.
- Example: Cross-check lesson plans with the EYLF or other relevant standards.
-
Quality Improvement Plan (QIP)
- Develop and update a QIP to track progress and set goals for continuous improvement.
- Example: Identify areas for enhancement and implement action plans to address them.
Further Reading
How To Achieve Quality Area 1
Reflection Questions For Quality Area 1
Exceeding Guidance For Quality Area 1
Documentation Services Require To Support Quality Area 1
Critical Reflection Questions For NQS QA1







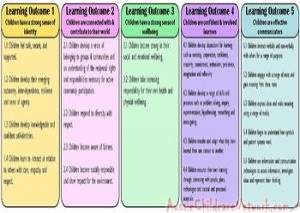 Here is the list of the EYLF Learning Outcomes that you can use as a guide or reference for your documentation and planning. The EYLF
Here is the list of the EYLF Learning Outcomes that you can use as a guide or reference for your documentation and planning. The EYLF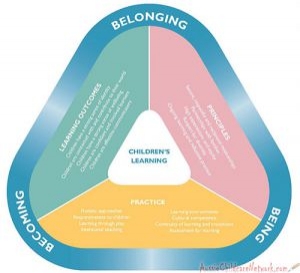 The EYLF is a guide which consists of Principles, Practices and 5 main Learning Outcomes along with each of their sub outcomes, based on identity,
The EYLF is a guide which consists of Principles, Practices and 5 main Learning Outcomes along with each of their sub outcomes, based on identity, This is a guide on How to Write a Learning Story. It provides information on What Is A Learning Story, Writing A Learning Story, Sample
This is a guide on How to Write a Learning Story. It provides information on What Is A Learning Story, Writing A Learning Story, Sample One of the most important types of documentation methods that educators needs to be familiar with are “observations”. Observations are crucial for all early childhood
One of the most important types of documentation methods that educators needs to be familiar with are “observations”. Observations are crucial for all early childhood To support children achieve learning outcomes from the EYLF Framework, the following list gives educators examples of how to promote children's learning in each individual
To support children achieve learning outcomes from the EYLF Framework, the following list gives educators examples of how to promote children's learning in each individual Reflective practice is learning from everyday situations and issues and concerns that arise which form part of our daily routine while working in an early
Reflective practice is learning from everyday situations and issues and concerns that arise which form part of our daily routine while working in an early Within Australia, Programming and Planning is reflected and supported by the Early Years Learning Framework. Educators within early childhood settings, use the EYLF to guide
Within Australia, Programming and Planning is reflected and supported by the Early Years Learning Framework. Educators within early childhood settings, use the EYLF to guide When observing children, it's important that we use a range of different observation methods from running records, learning stories to photographs and work samples. Using
When observing children, it's important that we use a range of different observation methods from running records, learning stories to photographs and work samples. Using This is a guide for educators on what to observe under each sub learning outcome from the EYLF Framework, when a child is engaged in
This is a guide for educators on what to observe under each sub learning outcome from the EYLF Framework, when a child is engaged in The Early Years Learning Framework describes the curriculum as “all the interactions, experiences, activities, routines and events, planned and unplanned, that occur in an environment
The Early Years Learning Framework describes the curriculum as “all the interactions, experiences, activities, routines and events, planned and unplanned, that occur in an environment


