Advantages Of Event Samples
- Facilitates effective collection of information to help inform Educators of possible triggers for an event/behaviour
- Simple and easy to use
- Builds up a picture of a specific behaviour
- They can be adapted to suit different circumstances
- The can be used to monitor progression and success towards any early intervention goals
Disadvantages Of Event Samples
- Time (Requires planning & preparation). Sometimes difficult to capture all that has occurred, particularly prior to an event.
- Needs a prepared chart and therefore cannot be spontaneous
- Charts needs to be carefully designed in order to collect the relevant information
- Data may not explain why the 'events' are occurring
When Should You Use Event Samples
- To observe and record how many times a child shows a specific action/behaviour
- To understand why a child may display such actions/behaviour
- To determine if their are any patterns or triggers to the action/behaviour
How To Record Event Samples
- A for Antecedent (possible triggers, behaviours, actions) immediately prior to the event;
- B for the Behaviour (a summary of the observed behaviour)
- C for the Consequences (what happened immediately after the behaviour/event.
Event samples are usually created using a grid or chart format. The way the grid/chart is set out will depend on the information required. Remember the event to be observed is decided in advance.
Sample 1

Sample 2
Event sample - frequency counts - involves observation of targeted behaviours or specific events. There is no recording of antecedents or consequences. The observer records a tally or tick every time a particular observable event or behaviour occurs.
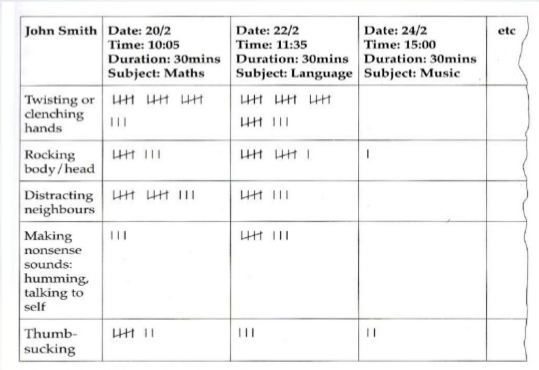
The information gathered through Event Samples will help you to assess what sparks a certain reaction in the child and identify the possible causes or consequences of concerning behaviour and find strategies to manage the behaviour effectively.
References:
Event Sampling Observation, Reference
Event Sample, Compliant Learning Resources
Observational Methods, Complex Needs UK







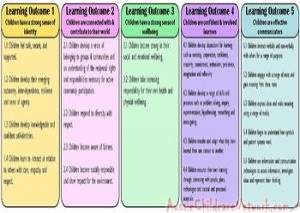 Here is the list of the EYLF Learning Outcomes that you can use as a guide or reference for your documentation and planning. The EYLF
Here is the list of the EYLF Learning Outcomes that you can use as a guide or reference for your documentation and planning. The EYLF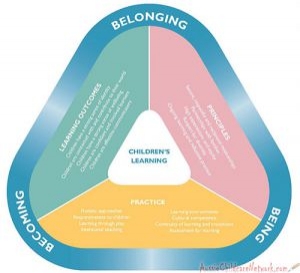 The EYLF is a guide which consists of Principles, Practices and 5 main Learning Outcomes along with each of their sub outcomes, based on identity,
The EYLF is a guide which consists of Principles, Practices and 5 main Learning Outcomes along with each of their sub outcomes, based on identity, This is a guide on How to Write a Learning Story. It provides information on What Is A Learning Story, Writing A Learning Story, Sample
This is a guide on How to Write a Learning Story. It provides information on What Is A Learning Story, Writing A Learning Story, Sample One of the most important types of documentation methods that educators needs to be familiar with are “observations”. Observations are crucial for all early childhood
One of the most important types of documentation methods that educators needs to be familiar with are “observations”. Observations are crucial for all early childhood To support children achieve learning outcomes from the EYLF Framework, the following list gives educators examples of how to promote children's learning in each individual
To support children achieve learning outcomes from the EYLF Framework, the following list gives educators examples of how to promote children's learning in each individual Reflective practice is learning from everyday situations and issues and concerns that arise which form part of our daily routine while working in an early
Reflective practice is learning from everyday situations and issues and concerns that arise which form part of our daily routine while working in an early Within Australia, Programming and Planning is reflected and supported by the Early Years Learning Framework. Educators within early childhood settings, use the EYLF to guide
Within Australia, Programming and Planning is reflected and supported by the Early Years Learning Framework. Educators within early childhood settings, use the EYLF to guide When observing children, it's important that we use a range of different observation methods from running records, learning stories to photographs and work samples. Using
When observing children, it's important that we use a range of different observation methods from running records, learning stories to photographs and work samples. Using This is a guide for educators on what to observe under each sub learning outcome from the EYLF Framework, when a child is engaged in
This is a guide for educators on what to observe under each sub learning outcome from the EYLF Framework, when a child is engaged in The Early Years Learning Framework describes the curriculum as “all the interactions, experiences, activities, routines and events, planned and unplanned, that occur in an environment
The Early Years Learning Framework describes the curriculum as “all the interactions, experiences, activities, routines and events, planned and unplanned, that occur in an environment


