

To Decision-Makers in Education and Care,
I write to you as an educator and advocate for the safety and well-being of children and staff in early childhood education.
Educator ratios must be upheld at all times, including during care tasks unless supervision is compromised, in which case coverage is legally required. Here’s a guide to help educators understand their rights and responsibilities around ratios and supervision, with more examples and direct links to authoritative sources.
In early childhood education, ratios are more than numbers. They are the heartbeat of safety, connection, and quality care. Yet across Australia, educators are sounding the alarm: current ratios are failing both children and staff. The sector is bleeding talent, and the emotional toll is mounting. It’s time to reform ratios—not just to meet minimum standards, but to honour the dignity of every child and the well-being of every educator.
In the wake of child abuse allegations and the rollout of policies like Four Eyes, early childhood educators are being asked to be more present, more vigilant, and more accountable. But presence alone is not enough. True safeguarding requires witnessing—not just watching. To witness is to be emotionally attuned, relationally responsive, and ethically grounded. It means seeing the child not as a subject of supervision, but as a whole person—worthy of affirmation, protection, and care.
Education Ministers have made safeguarding practices a national priority. As part of this, they’ve asked ACECQA to conduct a rapid assessment of how educator-to-child ratios are being applied in practice under the National Quality Framework.
In early childhood education, two terms often surface in compliance conversations: active supervision and in ratio. While both are essential to child safety and regulatory integrity, they serve distinct purposes—and conflating them can lead to serious oversights in practice. Let’s unpack each concept, then explore how they play out in real-world settings.
A: Legally, yes—an educator is considered “in ratio” as long as they are physically present and supervising the required number of children according to the age-based ratios set by the National Quality Framework (NQF). But practically? That’s where the system starts to unravel.
Early childhood educators and advocates have welcomed a sweeping $189 million reform package unveiled by federal, state, and territory education ministers, which includes a long-awaited review of staffing ratios and regulatory loopholes. Among the most significant developments is the decision to examine the controversial “under the roof” ratio—a practice that has long drawn criticism for compromising child safety and supervision.
Across the early childhood education and care sector, educators are sounding the alarm: current staffing ratios are insufficient to deliver safe, meaningful, and developmentally appropriate care. While recent reforms have focused on mobile phone bans and child safety protocols, many in the sector argue that these measures overlook a deeper structural issue—chronic understaffing driven by profit-based ratio models.
Dear Supporters,
Thank you for continuing to stand with us in the call to close the “Under the Roof” loophole in early childhood staffing ratios. Your voices have helped bring national attention to a regulatory gap that affects child safety, educator wellbeing, and sector integrity.
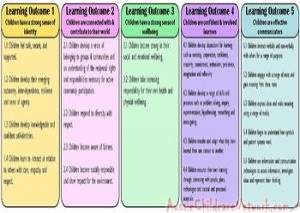 Here is the list of the EYLF Learning Outcomes that you can use as a guide or reference for your documentation and planning. The EYLF… Read More
Here is the list of the EYLF Learning Outcomes that you can use as a guide or reference for your documentation and planning. The EYLF… Read More
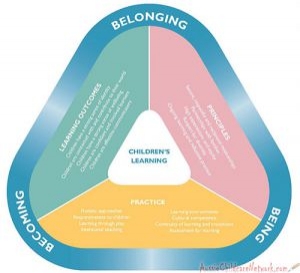 The EYLF is a guide which consists of Principles, Practices and 5 main Learning Outcomes along with each of their sub outcomes, based on identity,… Read More
The EYLF is a guide which consists of Principles, Practices and 5 main Learning Outcomes along with each of their sub outcomes, based on identity,… Read More
 This is a guide on How to Write a Learning Story. It provides information on What Is A Learning Story, Writing A Learning Story, Sample… Read More
This is a guide on How to Write a Learning Story. It provides information on What Is A Learning Story, Writing A Learning Story, Sample… Read More
 One of the most important types of documentation methods that educators needs to be familiar with are “observations”. Observations are crucial for all early childhood… Read More
One of the most important types of documentation methods that educators needs to be familiar with are “observations”. Observations are crucial for all early childhood… Read More
 To support children achieve learning outcomes from the EYLF Framework, the following list gives educators examples of how to promote children's learning in each individual… Read More
To support children achieve learning outcomes from the EYLF Framework, the following list gives educators examples of how to promote children's learning in each individual… Read More
 Reflective practice is learning from everyday situations and issues and concerns that arise which form part of our daily routine while working in an early… Read More
Reflective practice is learning from everyday situations and issues and concerns that arise which form part of our daily routine while working in an early… Read More
 Within Australia, Programming and Planning is reflected and supported by the Early Years Learning Framework. Educators within early childhood settings, use the EYLF to guide… Read More
Within Australia, Programming and Planning is reflected and supported by the Early Years Learning Framework. Educators within early childhood settings, use the EYLF to guide… Read More
 When observing children, it's important that we use a range of different observation methods from running records, learning stories to photographs and work samples. Using… Read More
When observing children, it's important that we use a range of different observation methods from running records, learning stories to photographs and work samples. Using… Read More
 This is a guide for educators on what to observe under each sub learning outcome from the EYLF Framework, when a child is engaged in… Read More
This is a guide for educators on what to observe under each sub learning outcome from the EYLF Framework, when a child is engaged in… Read More
 The Early Years Learning Framework describes the curriculum as “all the interactions, experiences, activities, routines and events, planned and unplanned, that occur in an environment… Read More
The Early Years Learning Framework describes the curriculum as “all the interactions, experiences, activities, routines and events, planned and unplanned, that occur in an environment… Read More

The approvals assessment process helps ensure all applicants, prior to approval, understand their responsibilities under...
See more...
Mindfulness can be incredibly beneficial for educators in early childhood settings. The following article provides...
See more...
A literacy-rich environment is one that gives children numerous opportunities to engage in emergent literacy...
See more...© 2009-2025 Aussie Childcare Network Pty Ltd. All Rights Reserved.

