

Our thoughts and deepest sympathies are with everyone affected by the tragic events at Bondi. We hold close in our hearts those who have suffered loss, those who were injured, and all families and community members navigating shock, grief, or uncertainty. In moments like these, we stand together in compassion, care, and solidarity.
When our wider community is shaken, children and families often look to us for steadiness, gentleness, and a sense of safety. Even when the world feels uncertain, the relationships we build in early childhood settings become powerful anchors.
As educators, we don’t need all the answers. What we can offer is presence, predictability, and compassion.
We know many of you are feeling unsure about what will happen to your pay once the Wage Increase Grant ends. This message is here to give you a clear, honest explanation so you know exactly what to expect.
Early childhood work is fast‑paced, relational, and constantly shifting. Good time management isn’t about squeezing more tasks into your day; it’s about creating space to be present with children, reducing overwhelm, and protecting your well-being.
This guide offers simple, educator‑friendly strategies that work in real rooms, with real children, and real staffing realities.
A: Roster changes can feel unsettling, especially when you’ve built routines around a regular day off. Here’s a simple breakdown to help you understand your rights and what usually happens in early childhood settings.
From 2026, every educator covered by the Children’s Services Award will move into a new, simplified classification structure. Instead of navigating 30 different levels, educators will transition into one of eight new Children's Services Employee (CSE) levels based on their qualification, experience, and role responsibilities.
This update doesn’t change the work you do; it simply ensures your classification and minimum pay rate accurately reflect the skills, knowledge, and responsibility you bring to your role. Whether you’re new to the sector, a Certificate III educator, a Diploma‑qualified educator, a room leader, or a director, you’ll be able to clearly see where you fit and what your new minimum rate will be by the end of the five‑year transition.
Below is an easy‑to‑read guide showing how each current classification translates into the new structure.
Provocations are not displays. They are not Pinterest‑perfect tableaus or aesthetic arrangements designed to impress adults. At their core, provocations are intentional invitations, carefully curated materials that nudge children toward exploration, questioning, and meaning‑making.
When we design with purpose, we shift from “setting up activities” to co-constructing possibilities. A well‑designed provocation whispers:
“I wonder what you’ll do with this…”
“What might you discover today…”
This shift honours children as thinkers, researchers, and capable contributors to their learning community.
When children dig, pour, smear, splash, squeeze, and explore, they’re not “making a mess.” They’re building the neural architecture that supports language, self-regulation, creativity, and problem‑solving. Sensory experiences are one of the most powerful, developmentally aligned ways children make sense of their world.
In early childhood education, we talk endlessly about teamwork, collaboration, and shared responsibility. But when the pressure hits, when a child is dysregulated, when an educator is overwhelmed, when the room feels like it’s tipping, the real test of teamwork appears.
And too often, what happens is this: People stand back. They watch. They wait. Sometimes out of uncertainty. Sometimes out of habit. Sometimes because they assume the educator “has it.”
But here’s the truth we need to say out loud: If you see a fellow educator is struggling, step in. Not later. Not when it escalates. Not when someone gets hurt. Now. We are human. We have limits. And we need each other.
Somewhere along the way, our sector slipped into a strange belief: if we don’t take hundreds of photos a week, we’re not doing our job.
But here’s the truth that many educators whisper quietly, often only to each other: We don’t need 200 photos to prove we’re educators.
We never did.
The heart of early childhood education has always been relationships, presence, and professional decision-making, not the size of a digital gallery.
An opinion article for early childhood educators exploring why excessive photo-taking doesn’t define quality practice. Highlights the importance of presence, intentional documentation, and sector-savvy approaches to capturing photos for families, observations, and learning documentation.
A practical, sector‑savvy guide for early childhood educators on understanding, navigating, and reducing workplace gossip (“bitching”). Includes examples, reflection prompts, and strategies to protect your energy and rebuild respectful team culture.
Gossip. Side comments. Whisper networks. The “Did you hear what she said?” moments that ripple through a service and drain the joy out of the day.
Every educator has felt it: the shift in the room when the bitching gets loud.
This isn’t about blaming individuals or shaming the workforce. It’s about understanding why gossip shows up, how it affects us, and what educators can do to protect their energy while still contributing to a respectful, professional culture.
This is a systemic issue, not a personal flaw, and when we name it honestly, we can finally start to shift it.
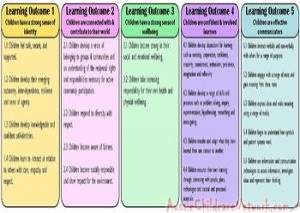 Here is the list of the EYLF Learning Outcomes that you can use as a guide or reference for your documentation and planning. The EYLF… Read More
Here is the list of the EYLF Learning Outcomes that you can use as a guide or reference for your documentation and planning. The EYLF… Read More
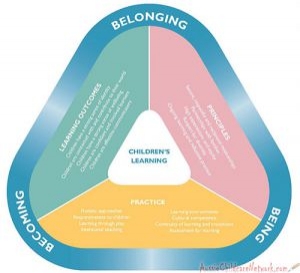 The EYLF is a guide which consists of Principles, Practices and 5 main Learning Outcomes along with each of their sub outcomes, based on identity,… Read More
The EYLF is a guide which consists of Principles, Practices and 5 main Learning Outcomes along with each of their sub outcomes, based on identity,… Read More
 This is a guide on How to Write a Learning Story. It provides information on What Is A Learning Story, Writing A Learning Story, Sample… Read More
This is a guide on How to Write a Learning Story. It provides information on What Is A Learning Story, Writing A Learning Story, Sample… Read More
 One of the most important types of documentation methods that educators needs to be familiar with are “observations”. Observations are crucial for all early childhood… Read More
One of the most important types of documentation methods that educators needs to be familiar with are “observations”. Observations are crucial for all early childhood… Read More
 To support children achieve learning outcomes from the EYLF Framework, the following list gives educators examples of how to promote children's learning in each individual… Read More
To support children achieve learning outcomes from the EYLF Framework, the following list gives educators examples of how to promote children's learning in each individual… Read More
 Reflective practice is learning from everyday situations and issues and concerns that arise which form part of our daily routine while working in an early… Read More
Reflective practice is learning from everyday situations and issues and concerns that arise which form part of our daily routine while working in an early… Read More
 Within Australia, Programming and Planning is reflected and supported by the Early Years Learning Framework. Educators within early childhood settings, use the EYLF to guide… Read More
Within Australia, Programming and Planning is reflected and supported by the Early Years Learning Framework. Educators within early childhood settings, use the EYLF to guide… Read More
 When observing children, it's important that we use a range of different observation methods from running records, learning stories to photographs and work samples. Using… Read More
When observing children, it's important that we use a range of different observation methods from running records, learning stories to photographs and work samples. Using… Read More
 This is a guide for educators on what to observe under each sub learning outcome from the EYLF Framework, when a child is engaged in… Read More
This is a guide for educators on what to observe under each sub learning outcome from the EYLF Framework, when a child is engaged in… Read More
 The Early Years Learning Framework describes the curriculum as “all the interactions, experiences, activities, routines and events, planned and unplanned, that occur in an environment… Read More
The Early Years Learning Framework describes the curriculum as “all the interactions, experiences, activities, routines and events, planned and unplanned, that occur in an environment… Read More

On the 20th of February every year, it is National Love Your Pet Day. This...
See more...
The EYLF Outcomes Meanings and Examples provide detailed meanings for each of the 5 learning...
See more...
Active Listening involves lending your undivided attention to someone who is speaking to you. As...
See more...© 2009-2025 Aussie Childcare Network Pty Ltd. All Rights Reserved.

