Quality Area 3 focuses on the physical environment in educational and care settings, as per frameworks like the National Quality Standard (NQS). It emphasizes creating safe, functional, and sustainable spaces that support learning and play. Here are some key terms associated with this area.
1. Sustainable Practices
Sustainable practices also include turning off lights when not in use, using rainwater tanks for irrigation, and involving children in recycling activities like sorting materials into proper bins. For example:
- A center installs a compost bin and teaches children how to compost food scraps during snack time. Educators explain the importance of reducing waste and show the children how compost helps plants grow in the garden.
2. Indoor and Outdoor Environments
A well-designed environment supports children’s exploration, creativity, and safety. Both environments should offer opportunities for solitary and group activities, ensuring children can learn and play in diverse ways. For example:
- Indoors, the center creates cozy corners with cushions and books for quiet reading. Outdoors, there’s a sensory garden with plants children can touch, smell, and observe. Play equipment is safe and age-appropriate, such as swings and climbing frames
3. Resources and Materials
Providing a variety of engaging materials that stimulate curiosity and learning. Regularly rotating materials keeps the environment fresh and exciting, encouraging children to discover new ways to use the resources. For example:
- The center provides natural materials like rocks, shells, and branches for children to explore. There’s also access to open-ended resources like playdough, building blocks, and art supplies for creative projects.
4. Accessibility
Spaces should be inclusive and cater to children of all abilities. Accessibility also includes considering cultural diversity, such as offering books and resources in multiple languages spoken by the children and their families. For example:
- The center designs ramps alongside stairs for children with mobility challenges. Furniture is child-sized, and resources are stored within easy reach so that all children can access them independently.
5. Risk Assessments
Risk assessments help educators create safe environments while allowing children to explore. For example:
- Before introducing a new water play area, educators identify potential hazards like slippery surfaces. They place non-slip mats, supervise children closely, and set clear safety rules to prevent accidents.
6. Natural Elements
Incorporating natural features encourages children to connect with and appreciate the environment. Natural elements like trees for shade, water features, and gardens not only enhance play but also support children’s understanding of sustainability and ecosystems. For example:
- The center has a mud kitchen where children mix soil, water, and leaves to “cook.” There’s also a bird feeder that children help fill, teaching them about local wildlife.
7. Flexible Layouts
Adaptable spaces allow for dynamic learning opportunities. Flexible layouts cater to changing group sizes and activities, ensuring the environment continues to meet the evolving needs of children. For example:
- An indoor playroom can be transformed into an art studio by rearranging tables and adding easels and paint supplies. Outdoor areas can be divided into zones for quiet activities like gardening and active play like running or jumping.
8. Aesthetic Appeal
Visually engaging and organized spaces create a sense of belonging and comfort for children. For example:
- Walls are decorated with children’s artwork, making them feel valued and proud. Shelves are arranged neatly with colorful bins labeled for toys and resources to promote organization.
9. Maintenance
Regular upkeep ensures environments are safe, clean, and functional. Maintenance also involves proactive measures, like replacing worn-out resources and updating spaces to reflect children’s interests or developmental needs. For example:
- The center has a checklist for daily and weekly maintenance tasks, such as inspecting play equipment, fixing broken toys, and cleaning surfaces and floors.
10. Eco-Friendly Initiatives
These initiatives promote environmental awareness and responsibility. Eco-friendly initiatives teach children to become environmentally conscious citizens and can extend to engaging families in sustainability efforts at home. For example:
- Children participate in planting trees during Earth Day celebrations and learn about the importance of reducing carbon footprints. Educators also use natural light and energy-efficient appliances to minimize power consumption.
These examples show how Quality Area 3 concepts are implemented to create enriching, safe, and sustainable environments for children.
Further Reading
Understanding Quality Areas
How To Achieve Quality Area 3
Reflection Questions For Quality Area 3
Exceeding Guidance For Quality Area 3
Documentation Services Are Require To Support Quality Area 3







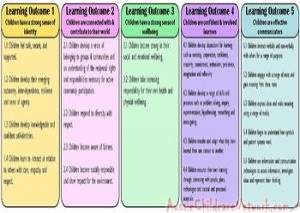 Here is the list of the EYLF Learning Outcomes that you can use as a guide or reference for your documentation and planning. The EYLF
Here is the list of the EYLF Learning Outcomes that you can use as a guide or reference for your documentation and planning. The EYLF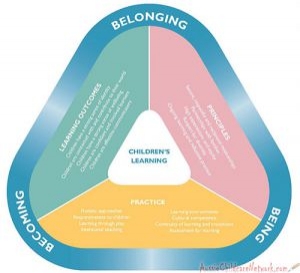 The EYLF is a guide which consists of Principles, Practices and 5 main Learning Outcomes along with each of their sub outcomes, based on identity,
The EYLF is a guide which consists of Principles, Practices and 5 main Learning Outcomes along with each of their sub outcomes, based on identity, This is a guide on How to Write a Learning Story. It provides information on What Is A Learning Story, Writing A Learning Story, Sample
This is a guide on How to Write a Learning Story. It provides information on What Is A Learning Story, Writing A Learning Story, Sample One of the most important types of documentation methods that educators needs to be familiar with are “observations”. Observations are crucial for all early childhood
One of the most important types of documentation methods that educators needs to be familiar with are “observations”. Observations are crucial for all early childhood To support children achieve learning outcomes from the EYLF Framework, the following list gives educators examples of how to promote children's learning in each individual
To support children achieve learning outcomes from the EYLF Framework, the following list gives educators examples of how to promote children's learning in each individual Reflective practice is learning from everyday situations and issues and concerns that arise which form part of our daily routine while working in an early
Reflective practice is learning from everyday situations and issues and concerns that arise which form part of our daily routine while working in an early Within Australia, Programming and Planning is reflected and supported by the Early Years Learning Framework. Educators within early childhood settings, use the EYLF to guide
Within Australia, Programming and Planning is reflected and supported by the Early Years Learning Framework. Educators within early childhood settings, use the EYLF to guide When observing children, it's important that we use a range of different observation methods from running records, learning stories to photographs and work samples. Using
When observing children, it's important that we use a range of different observation methods from running records, learning stories to photographs and work samples. Using This is a guide for educators on what to observe under each sub learning outcome from the EYLF Framework, when a child is engaged in
This is a guide for educators on what to observe under each sub learning outcome from the EYLF Framework, when a child is engaged in The Early Years Learning Framework describes the curriculum as “all the interactions, experiences, activities, routines and events, planned and unplanned, that occur in an environment
The Early Years Learning Framework describes the curriculum as “all the interactions, experiences, activities, routines and events, planned and unplanned, that occur in an environment


