A food allergy is a hypersensitive reaction to a normally harmless substance in food and is quite common in babies and children. Some children are more likely to have an allergic reaction triggered by a particular food. Those most at risk are babies and children from families with a history of allergies. By the time a child is 2 years old they would have more than likely grown out of their allergy. However other children will have a food allergy throughout their life.
What Causes a Food Allergy?
A food allergy is an adverse immune response to a food protein. These kinds of allergies occur when the body's immune system mistakenly identifies a protein as harmful. Some proteins or fragments of proteins are resistant to digestion and those that are not broken down in the digestive process are tagged by the Immunoglobulin E (IgE). These tags fool the immune system into thinking that the protein is an invader. The immune system, thinking the organism (the individual) is under attack, sends white blood cells to attack, and that triggers an allergic reaction.
Allergy Reactions
These reactions can range from mild to severe. Allergic responses include dermatitis, gastrointestinal and respiratory distress, including such life-threatening anaphylactic responses as biphasic anaphylaxis and vasodilatation; these require immediate emergency intervention. Individuals with protein allergies commonly avoid contact with the problematic protein. Some medications may prevent, minimize or treat protein allergy reactions. There is no cure.
Signs and Symptoms
Classic immunoglobulin-E (IgE)-mediated food allergies are classified as type-I immediate Hypersensitivity reaction. These allergic reactions have an acute onset (from seconds to one hour) and may include:
- Hives
- Itching of mouth, lips, tongue, throat, eyes, skin, or other areas
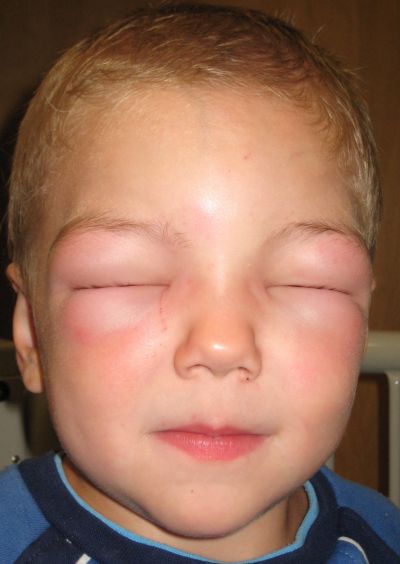
- Swelling (angioedema) of lips, tongue, eyelids, or the whole face
- Difficulty swallowing
- Runny or congested nose
- Hoarse voice
- Wheezing and/or shortness of breath
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Abdominal pain and/or stomach cramps
- Lightheadedness
- Fainting
- Death
- Symptoms of allergies vary from person to person. The amount of food needed to trigger a reaction also varies from person to person
Common Food Allergies
Below is a list of most common food allergies found in babies and children. In addition to these you should be careful with sesame seeds and products made from them, soya products and fish (especially shell fish). Please remember that this is to be used as a general guide only and if you have any concerns, please consult your doctor.
Peanuts and Other Nuts
Reaction Caused:
Anaphylactic shock (causing breathing difficulty and throat to swell)
Avoid:
- Peanuts
- Peanut Butter
- Unrefined Peanut Oil
Dairy Products
Reaction Caused:
- Tummy aches
- Diarrhoea
- Anaphylactic Shock
Avoid:
- Cow's milk
- Cheese
- Butter
Gluten
Reaction Caused:
- Diarrhoea
- Tummy aches
- Weight loss
- Damaging of intestine lining
- Anaphylactic Shock
Avoid:
- Wheat
- Bread
- Pasta
- Cakes
- Flour
- Barley
- Rye
- Oats
Eggs
Reaction Caused:
- Rashes
- Eczema
- Skin swellings
- Tummy ache
- Anaphylactic Shock
Avoid:
- Eggs
- Egg whites
- Cakes
- Breads (contain egg)
- Cake (contain egg)
Tomatoes
Reaction Caused:
- Rash
- Eczema
- Anaphylactic Shock
Avoid:
- Tomatoes
- Tomato sauce
- Canned tomatoes
- Tomato pasta sauce
Citrus Fruit and Strawberries
Reaction Caused:
- Rash
- Eczema
- Anaphylactic Shock
Avoid:
- Fresh oranges
- Orange lollies
- Fruit yoghurt
- Squash
If you think your child is reacting to a certain food - with pain, diarrhoea, rashes or vomiting after eating – even though you may have no family history of allergies, trust your instincts and go straight to the hospital.
References
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Food_allergy